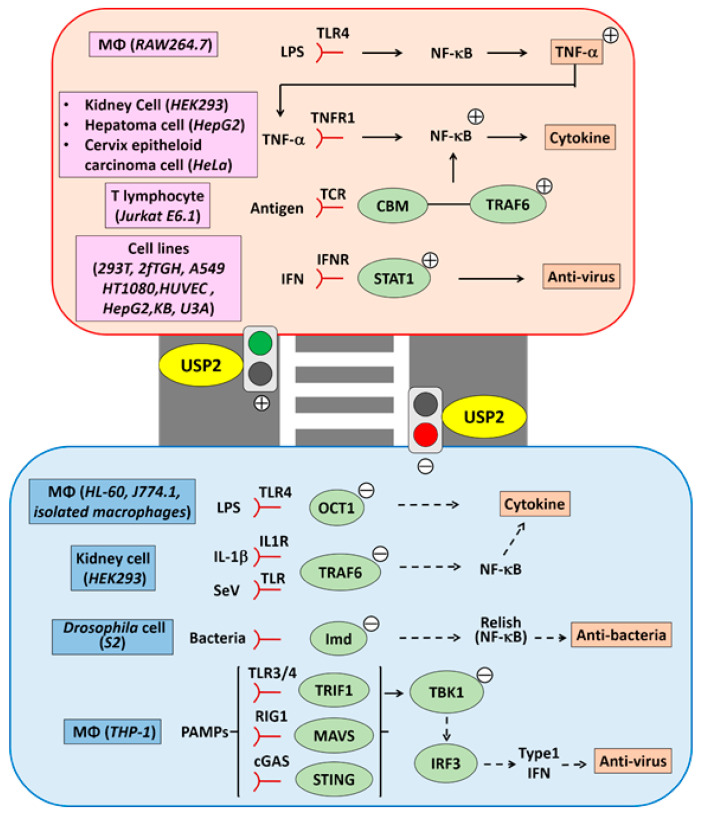
Figure 3.
Roles of USP2 in immune and inflammatory responses. Previous reports indicate that USP2 exerts both positive and negative effects on immune and inflammatory responses. USP2 stabilizes TNF-α and the TNF-α–elicited signaling complex, leading to activation of NF-κB. USP2 also potentiates NF-κB activation in T-lymphocytes via the interaction between the CBM complex and TRAF6. Moreover, USP2 stimulates nuclear accumulation of STATs, which promotes antiviral activity in cells. In contrast, there are papers demonstrating that USP2 modifies OCT1, TRAF6, and Imd (Drosophila orthologue of RIP1) to suppress the expression of proinflammatory cytokines and anti-bacterial peptides. Additionally, USP2 modulates TBK1 to attenuate signaling along the RIGI, cGAS/STING, and TRIF pathways. USP2-elicited attenuation of TBK1 also lowered IRF3 activation, resulting in decreased IFNβ production.