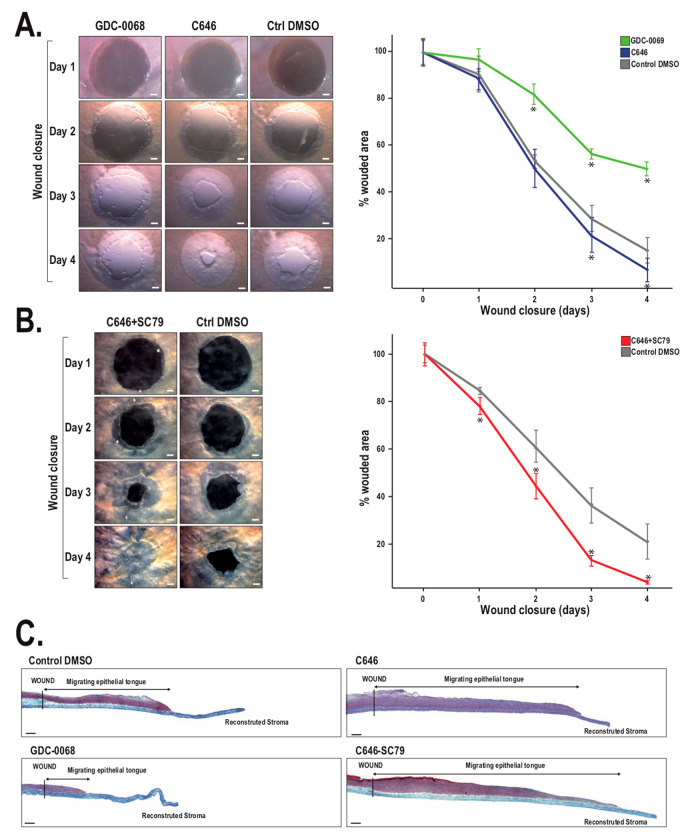
Figure 6.
Impact of GDC-0068, C646, and SC79 on wound closure of human TECs. (A) Human TECs (one out of four representative hTECs is shown for each condition) were wounded and maintained in culture medium supplemented with GDC-0068 or C646 (left). Wound surfaces remaining for each condition were determined at each day and plotted on the graph (right). Control wounded hTECs were exposed solely to the vehicle (DMSO). Scale bars: 1 mm. (B) Wounded hTECs were incubated with both C646 and SC79 (left); one out of six representative hTECs is shown for each condition). Wound surfaces remaining were determined at each day and plotted on the graph (right). Control wounded hTECs were exposed solely to the vehicle (DMSO). Scale bars: 1 mm. (C) Composite images showing a complete histological view of wounded TECs grown in the presence of GDC0068, C646, or both the combination of C646 and SC79 at 4 days following corneal damage (sections were stained with Masson trichrome; cells are pink, and collagen is bluish). The wound margin created by the biopsy punch is indicated. Scale bar: 100 μm (Figure adapted from Reference [171] with the permission of the journal ACTA Biomaterialia).