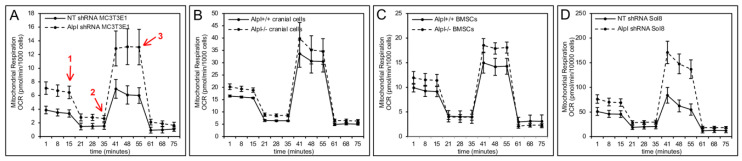
Figure 7.
TNAP deficiency increases mitochondrial respiration and oxygen consumption rate. Seahorse XF cell mito stress tests (Agilent) were performed to confirm an effect of TNAP on live cell metabolic activity. Red arrows demark when cells are exposed to respiration modulators. 1 = oligomycin (inhibits ATP synthase; reflects loss of ATP linked respiration); 2 = FCCP (disrupts the mitochondrial membrane potential; reflects maximal respiration); 3 = Rotenone + Antimycin (inhibit mitochondrial proton pumps; reflect nonmitochondrial respiration driven by processes outside the mitochondria). Minutes 1–15 reflect basal cellular oxygen consumption rate (OCR). Minutes 15–35 reflect loss of ATP linked OCR. Minutes 41–55 reflect maximal OCR. Basal and maximal OCR appear increased in in Alpl shRNA treated vs. non-target shRNA MC3T3E1 cells (A), in Alpl−/− vs. Alpl+/+ primary cranial osteoprogenitor cells (B), in Alpl−/− vs. Alpl+/+ BMSCs (C), and in Alpl shRNA treated vs. non-target shRNA Sol8 skeletal progenitor cells (D). n = 3 per genotype per experiment. Statistical comparisons for key parameters of mitochondrial function are shown in Table 1.