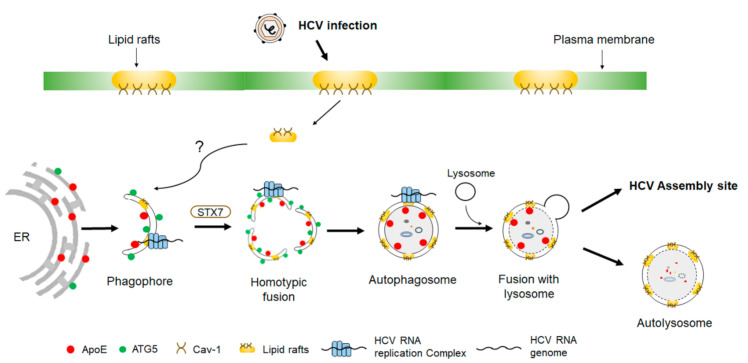
Figure 2.
Biogenesis of autophagosomes induced by HCV. Phagophores induced by HCV originate from the ER membranes. The HCV RNA replication complex as well as its associated lipid rafts and caveolin-1 (Cav-1) become associated with phagophores through an unknown mechanism. Phagophores subsequently undergo homotypic fusion in a process dependent on syntaxin 7 (STX7) to form autophagosomes. During these processes, apolipoprotein E (ApoE) becomes associated with autophagosomes and is delivered by autophagosomes to the HCV assembly site to interact with the HCV E2 envelope protein. Some of the autophagosomes may also fuse with lysosomes to form autolysosomes to result in the autophagic degradation of ApoE.