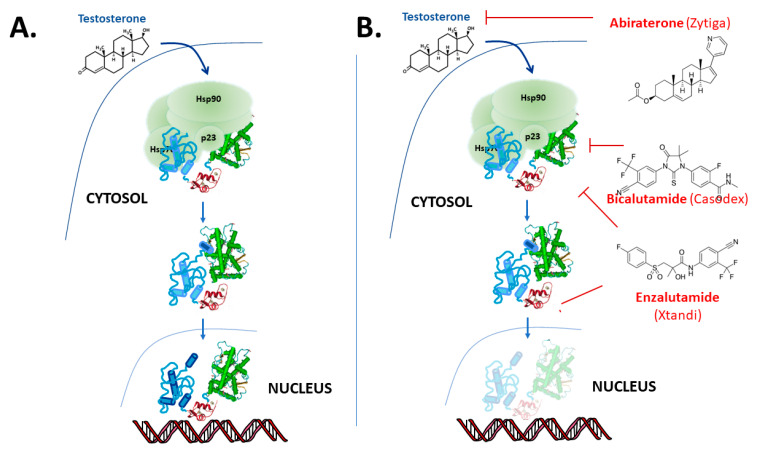
Figure 2.
Overview of androgen receptor mechanism of action. (A) In the “classical” model the AR binds to testosterone and in tissues such as the prostate preferentially to the more potent metabolite 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and dissociates from molecular chaperones and translocates to the nucleus where it binds to DNA response elements and up- or down-regulates target gene expression. However, the details of a number of these steps in this model remain subject to debate and on-going research. (B) The action of the drugs abiraterone, bicalutamide and enzalutamide used in the treatment of PCa.