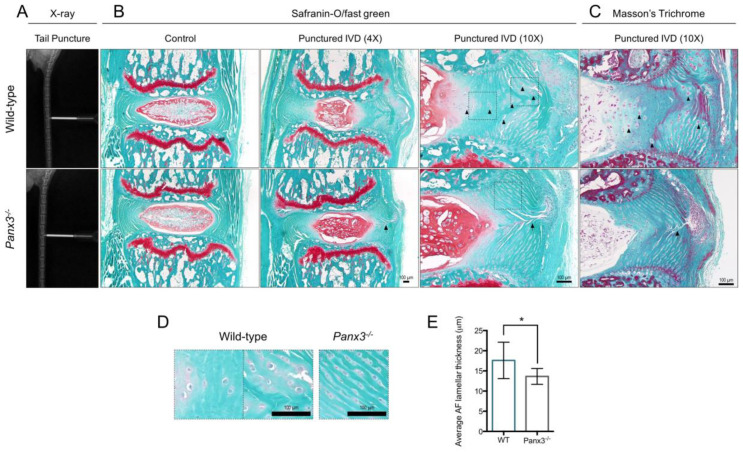
Figure 5.
Panx3-/- mice maintain AF tissue architecture following NP depressurization of caudal IVDs. (A) Representative X-ray images of WT and Panx3-/- caudal IVDs undergoing needle puncture. (B,C) Representative mid-sagittal sections of caudal IVDs 7/8 and 8/9 from WT and Panx3-/- mice harvested 6-weeks following needle puncture stained with (B) safranin-O/fast green and (C) Masson’s Trichrome. Adjacent, uninjured caudal IVD 6/7 served as the control. Images representative of n = 6 mice per group, 2 IVDs per mouse. Arrowheads indicate enlarged AF cells detected in WT mice following injury, arrows mark the needle puncture track. (D) Magnified view of AF cells in WT and Panx3-/- caudal IVDs 6-weeks following needle puncture. Images correspond to areas indicated by boxes in panel B. (E) Average AF lamellar thickness in WT and Panx3-/- IVDs following needle puncture injury. Lamellar thickness (inclusive of lamellar and inter-lamellar widths) was measured throughout the AF of Mason’s Trichrome stained caudal IVDs post-puncture and averaged per IVD. (* indicates, p < 0.05, unpaired t-test; n = 6 mice per group, 2 IVDs per mouse).