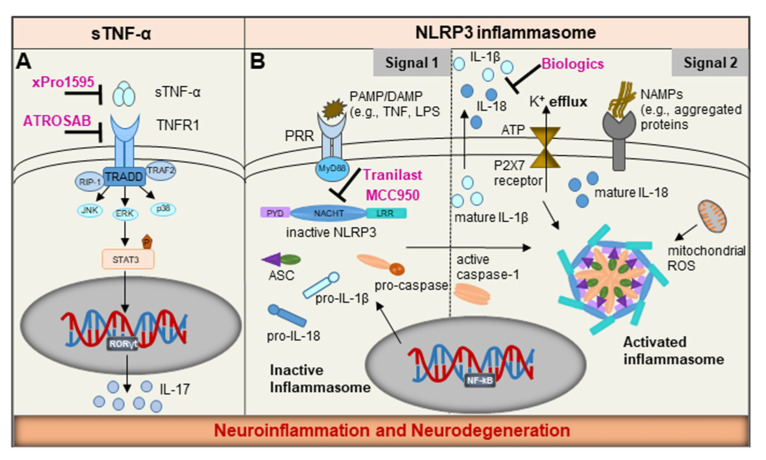
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of potential therapeutic approaches targeting common pathways in mast cells and microglia. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) signaling and the NLRP3 inflammasome, represent the two common pathways that can be targeted to dampen inflammation. (A) ATROSAB, a TNFR1-specific antagonist and xPro1595, a neutralizing antibody specifically inhibit soluble TNF-α; (B) Biologics, namely recombinant IL-1β receptor antagonist (Anakinra), IL-1β neutralizing antibody (Canakinumab) and a soluble decoy receptor that binds IL-1β (Rilonacept) are in clinical use. Tranilast (Rizaben) and MCC950 have been identified as specific inhibitors that binds to the NOD domain (also referred as the NACHT domain) of the NLRP3 and inhibit inflammasome assembly and activation, in turn, inhibiting the vicious cycle of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.