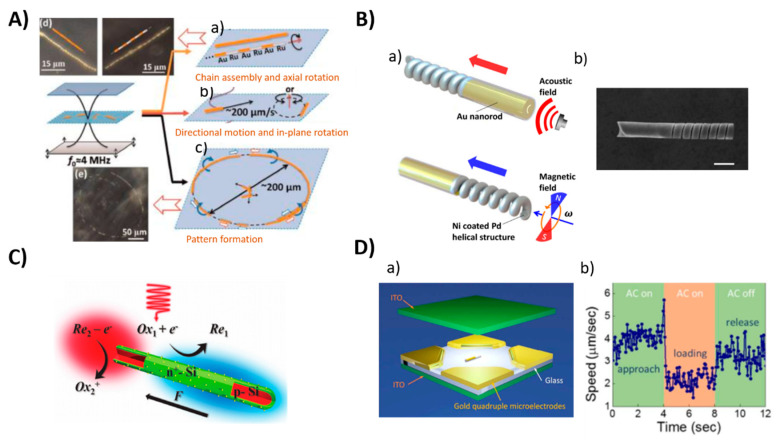
Figure 6.
Examples of different propulsion strategies of nanomotors powered by an external sources (A) Ultrasound, (a–c): schematic illustration of the motions of metal microrods in a 3.7 MHz acoustic field. Shown motion: axial, directional motion, in-plane rotation, chain assembly, axial spinning, and pattern formation, especially ring patterns (d,e): Dark field images of typical chain structures and ring patterns that were formed by Au and AuRu rods. Reproduced from [95] with permission of the American Chemical Society. (B) Magnetic: (a) Scheme of hybrid magneto-acoustic nanomotors and dual propulsion mode driven by magnetic and ultrasound fields. (b) SEM image of a magneto−acoustic hybrid nanomotor. Scale bar: 500 nm. Reproduced from [107] with permission of the American Chemical Society. (C) Light: Schematic illustration of the light-driven nanomotor. An n+-Si (green) shell was formed on a p-Si core (red) by thermal diffusion doping of phosphorous and platinum (yellow) nanoparticles were deposited on the surface as an electrocatalyst. Reproduced from [108] with permission of WILEY-VCH. (D) Electric field: (a) Scheme of 3-D orthogonal microelectrode setup (b) Speed of the nanomotor in the cargo delivery process. Reproduced from [109] with permission of American Chemical Society.