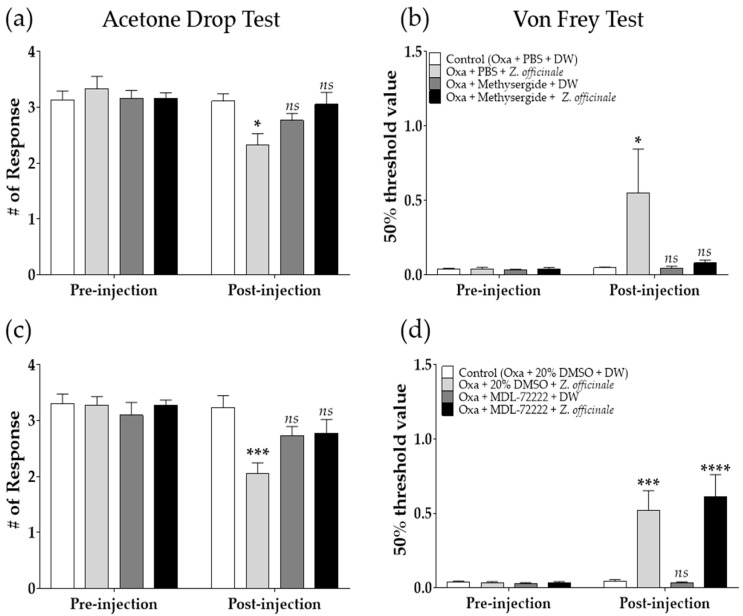
Figure 3.
Effect of intrathecal administration of serotonin receptor antagonists on the analgesic effect of Z. officinale against oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic pain. The effect of methysergide (a,b) and MDL-72222 (c,d) on Z. officinale-induced inhibition of cold (a,c) and mechanical (b,d) allodynia. When significant allodynic signs were observed in oxaliplatin-treated mice, methysergide or MDL-72222 was injected intrathecally in mice. PBS or 20% DMSO was used as a control for methysergide and MDL-72222, respectively. Z. officinale or DW was administered orally 20 min after the administration of methysergide, MDL-72222, PBS, or 20% DMSO. Pre-injection: before the injection of PBS, methysergide, 20% DMSO, MDL-7222, and Z. officinale. Post-injection: After the injection of PBS, methysergide, 20% DMSO, MDL-7222, and Z. officinale. Cold and mechanical allodynia were assessed by using the acetone drop and von Frey filament tests, respectively. Control (Oxa + PBS + DW): n = 6, Oxa + PBS + Z. officinale: n = 6, Oxa + Methysergide + DW: n = 5, Oxa + Methysergide + Z. officinale: n = 6 (a, b). Control (Oxa + 20% DMSO + DW): n = 6, Oxa + 20% DMSO + Z. officinale: n = 6, Oxa + MDL-72222 + DW: n = 6, Oxa + MDL-72222 + Z. officinale: n = 6 (c, d). ns: non-significant, * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 vs. Control (Oxa + PBS + DW or Oxa + 20% DMSO + DW) with two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post-test for multiple comparisons.