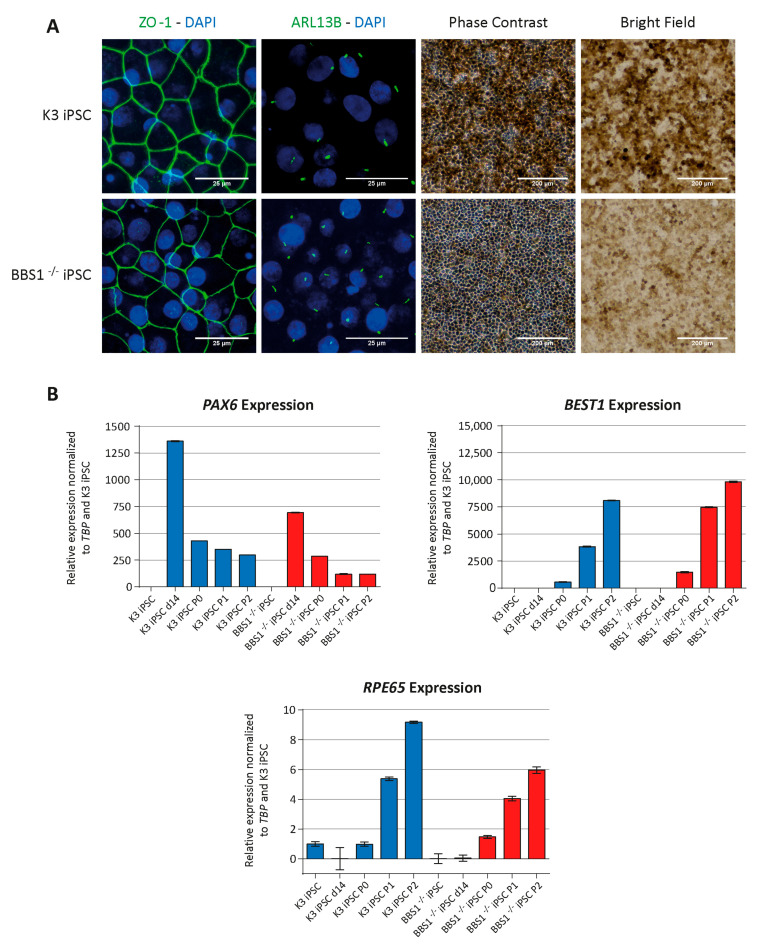
Figure 4.
Differentiation of BBS1-iPSC into RPE-like cells. Control K3 iPSC and BBS1−/− iPCS were analyzed for RPE phenotype, after differentiation for 110 days (end of P2). (A) IFM after incubation with antibodies against ZO-1 (tight junction marker) and ARL13B (Cilia marker). Nuclei were visualized with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining (Panels 1 and 2), scale bar 25 µM. Phase contrast pictures (Panel 3), scale bar 200 µM. Bright-field images (Panel 4), scale bar 200 µM. Both control K3 iPSC and BBS1−/− iPCS were able to form tight junctions (Panel 1) and primary cilia (Panel 2). The cells had obtained the characteristic cobblestone morphology of RPE cells (Panel 3). Both cell-lines became pigmented (Panel 4). (B) Gene Expression. mRNA was isolated at different time points during the differentiation process and quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) was performed. mRNA was isolated at day 0 (iPSC clone), day 14 after initiation of differentiation (d14) and at the end of the three passages, P0, P1 and P2. Expression profile of PAX6 (retinal precursor marker), BEST1 (mature RPE marker) and RPE65 (mature RPE marker) was normalized to the expression of the endogenous TBP gene encoding the TATA-box binding protein. Data derived from one experiment (technical triplicates); no statistics performed.