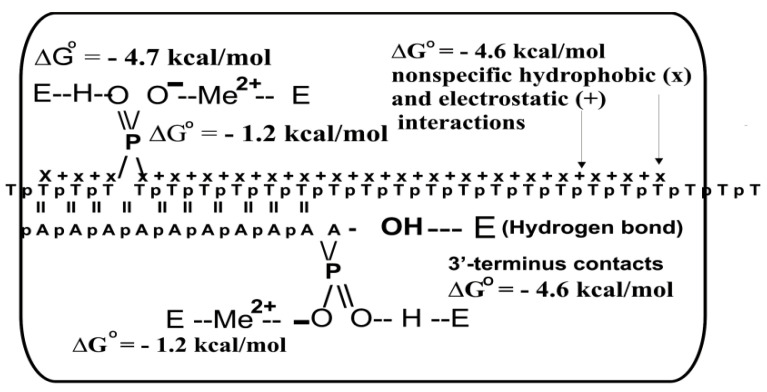
Figure 2.
A thermodynamic model for the interaction of human DNA polymerase α with d(pT)20 × d(pA)10 [20,21]. It can be seen that the globule of DNA polymerase covers 20 nucleotide units of the template and 10 nucleotides of complementary primer. Bases of the template and 19 out of 20 internucleoside groups form weak additive contacts with the template-binding site of the enzyme (total ΔG° = −4.6 kcal/mol), while one internucleoside phosphate group of the template has strong contacts—one hydrogen bond and one electrostatic contact (total ΔG° = −4.7 kcal/mol). Only the 3′- terminal unit of the primer makes contacts with the enzyme, forming ONE hydrogen bond WITH THE 3′-OH primer group and two contacts WITH THE FIRST from the 3′-end internucleoside phosphate group (total ΔG° = −4.6 kcal/mol). The rest of the primer nucleotide units interact only with the complementary template through the formation of Watson–Crick hydrogen bonds.