Fig. 7.
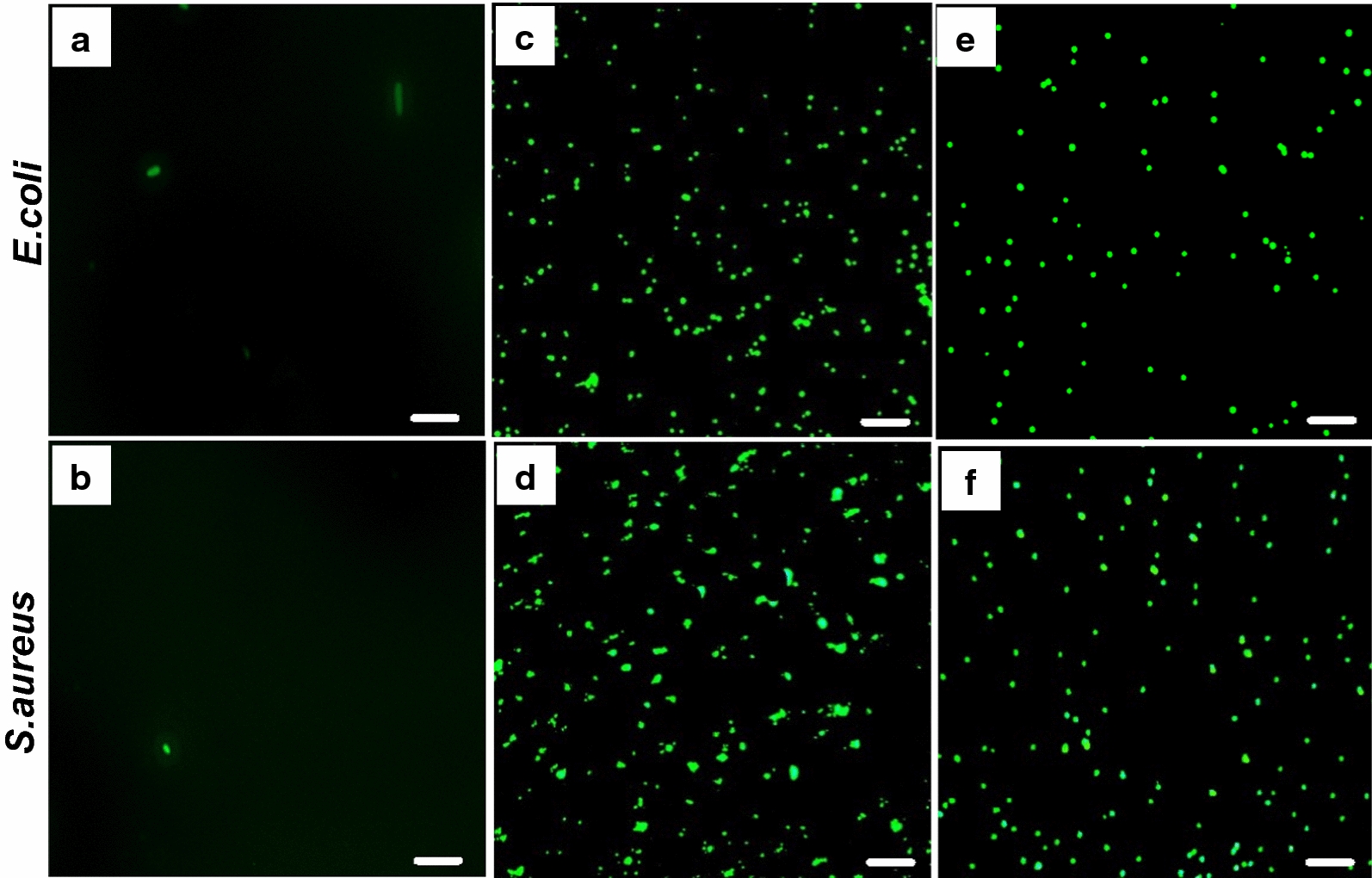
Membrane permeability assay. Fluorescence images of E. coli and S. aureus showing the influx of FITC after treatment with zinc ferrite (ZnFe2O4) NPs and tetracycline (positive control). a Untreated E. coli (negative control). b Untreated S. aureus (negative control). c E. coli treated with tetracycline (positive control). d S. aureus treated with tetracycline (positive control). e E. coli treated with 100 µg/mL of ZnFe2O4 NPs. f S. aureus treated with 100 µg/mL of ZnFe2O4 NPs. Tetracycline and ZnFe2O4 NPs induced membrane damage to both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, resulted in the membrane permeability to the green fluorescent FITC dye. Scale bars show 100 µm
