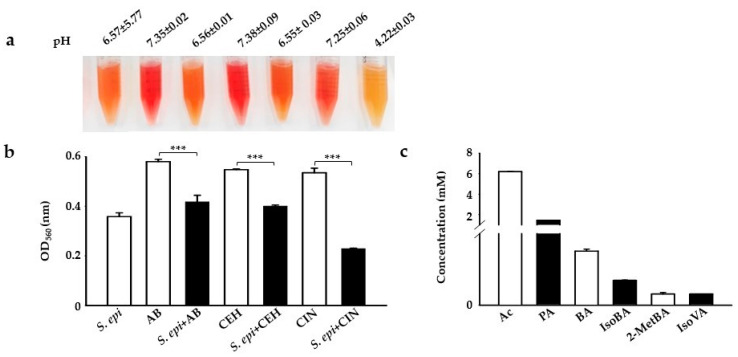
Figure 1.
S. epidermidis mediates triggers CIN fermentation to produce SCFAs. (a) S. epidermidis (S. epi) (ATCC 12228) (107 CFU/mL) was incubated in rich media containing phenol red with and without 2% AB, CEH, and CIN for 12 h. Rich media with phenol red plus 2% AB, CEH, or CIN were included as a control. The pH values of S. epi, AB, S.epi+AB, CEH, S.epi+CEH, CIN, and S.epi+CIN were 6.57 ± 5.77, 7.35 ± 0.02, 6.56 ± 0.01, 7.38 ± 0.09, 6.55 ± 0.03, 7.25 ± 0.06, and 4.22 ± 0.03, respectively. Bacterial fermentation was indicated by the color change of phenol red to yellow. (b) A graph showing the OD560 (nm) value in all the above groups. (c) The graph represents the amount of SCFAs generated from CIN fermentation by S. epi by GC-MS analysis. The x-axis represents the type of SCFAs used in the fermentation: Ac, acetic acid; BA, butyric acid; PA, propionic acid; IsoBA, isobutyric acid; 2MetBA, 2-methyl butyric acid; and IsoVA, isovaleric acid. The y-axis is their concentration in millimolars (mM). Data are expressed as means ± SD. (*** p < 0.001; n = 3).