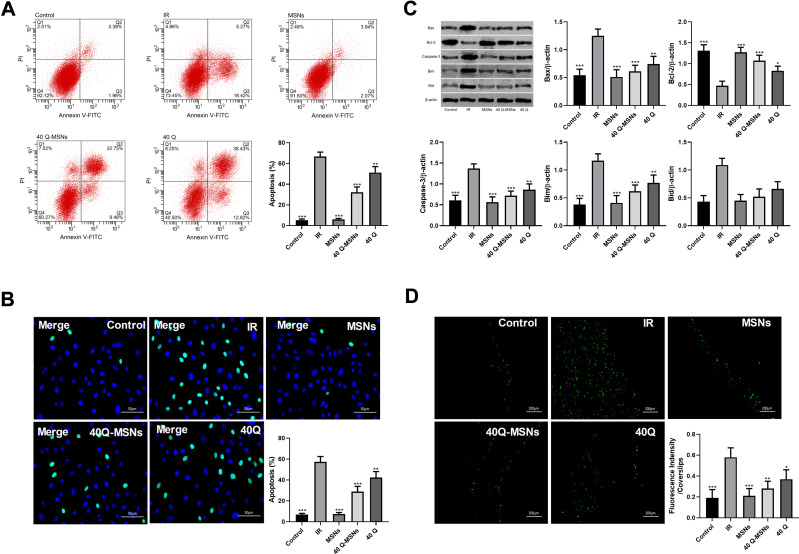
Figure 2.
Effect of Q-MSNs on apoptosis and oxidative stress of hypoxia/reoxygenation myocardial cells. (A) Cell apoptosis in each group determined by annexin V/PI staining. There was inhibition on cell apoptosis in both Q group and Q-MSNs group. At the same concentration, the inhibitory effect in the 40Q-MSNs group was better, and silica nanoparticles alone had no effect on apoptosis. (B) Cell apoptosis in each group determined by Tunel staining. There was inhibition on cell apoptosis in both Q group and Q-MSNs group. At the same concentration, the inhibitory effect in the 40Q-MSNs group was better. (C) Apoptosis-related proteins in cells determined by Western blotting.There was regulation on apoptosis-related proteins in cells in both the Q group and Q-MSNs group, and at the same concentration, the regulation effect in the 40Q-MSNs group was better. (D) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in each group. There was inhibition on the production of ROS in cells in both Q group and Q-MSNs group, and at the same concentration, the inhibitory effect in the 40Q-MSNs group was better.
Notes: Primary myocardial cells were sampled from SD neonatal rats at 8–15 days old, and their apoptosis and ROS level were determined after hypoxia/reoxygenation treatment. Each experiment was repeated 3 times. Compared with the IR group, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
Abbreviations: MSNs, mesoporous silica nanoparticles without quercetin; 40Q-MSNs, 40 μmol/L quercetin-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles; 40Q, 40 μmol/L quercetin; IR, ischemia reperfusion.