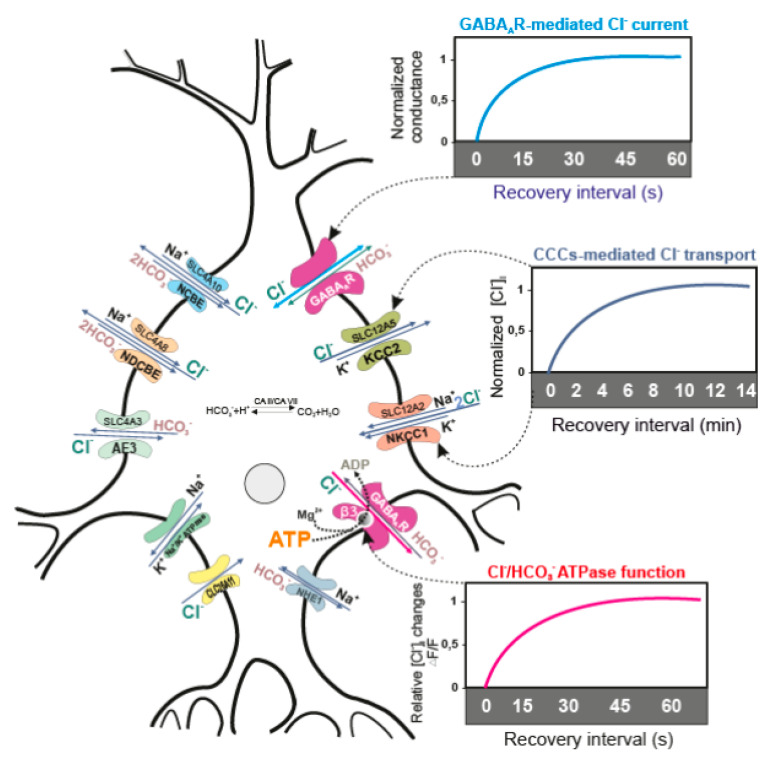
Figure 1.
Performance of transporters and recovery of the receptor function. Neuronal [Cl−]i is maintained mainly by neutral active CCCs (KCC2 and NKCC1), and less by Cl− channels (SLC26 family) and exchangers (SLC4 family—AE3, NCBE or NDCBE). CCCs move the Cl− ions by utilizing the energy electrochemical Na+ and K+ gradient, whose maintenance involves Na+, K+ATPase. CCCs need at least 5 min to recover [Cl−]i [48,57,68,69,70,71], while the GABAAR-mediated conductance may recover during approximately 10–15 s after [Cl−]i changes [51,61]. After purification and reconstitution into proteoliposomes, the β3-containing GABAAR homopentamer participates in ATP-consuming Cl− transport for a short period (~30 s) and then reaches a plateau [35]. The bottom panel shows the changes of [Cl−]i after application of Mg2+-ATP in the experimental medium containing proteoliposomes with embedded GABAAR/Cl−, HCO3−ATPase, as well as the fluorescent dye for chloride.