Figure 4. Mucolytic therapy decreases mucinous tumor growth in a mouse PDX model of early MCP.
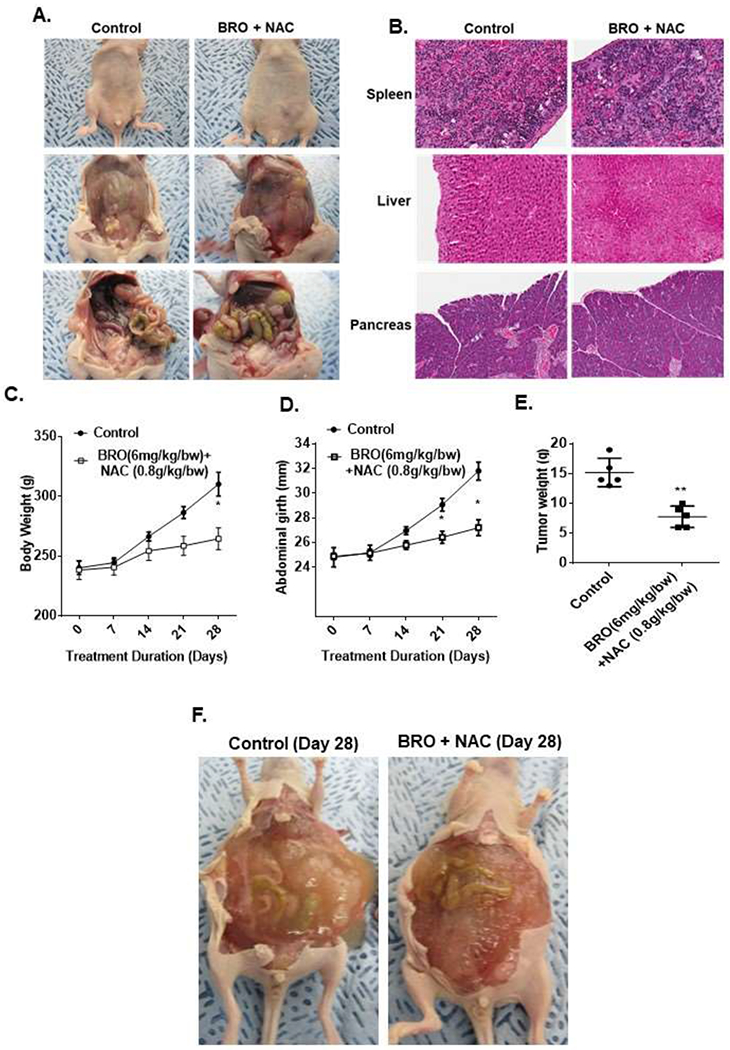
Non-tumor bearing nude mice were administered 200 μl of BRO (6 mg/kg bw) + NAC (0.8 g/kg bw) solution (in PBS, pH 8.0) or PBS (control) IP every other day for 2 weeks; gross evaluation (A) and pathological microscopic evaluation of abdominal organs (with H&E staining) (B) for toxicity is shown. Early MCP model of IP mucolytic (versus control) therapy, at same dose/frequency as in toxicity studies, demonstrating serial changes in gross body weight (C) and abdominal girth (D); and abdominal tumor content weight following sacrifice at day 28 (E). Late (advanced) MCP model of IP mucolytic (versus control) therapy showing gross pictures of advanced tumor burden unresponsive to mucolytic therapy at day 28 (F). Error bars represent standard deviation (SD) from triplicate experiments (*P< .05, **P< .01).
