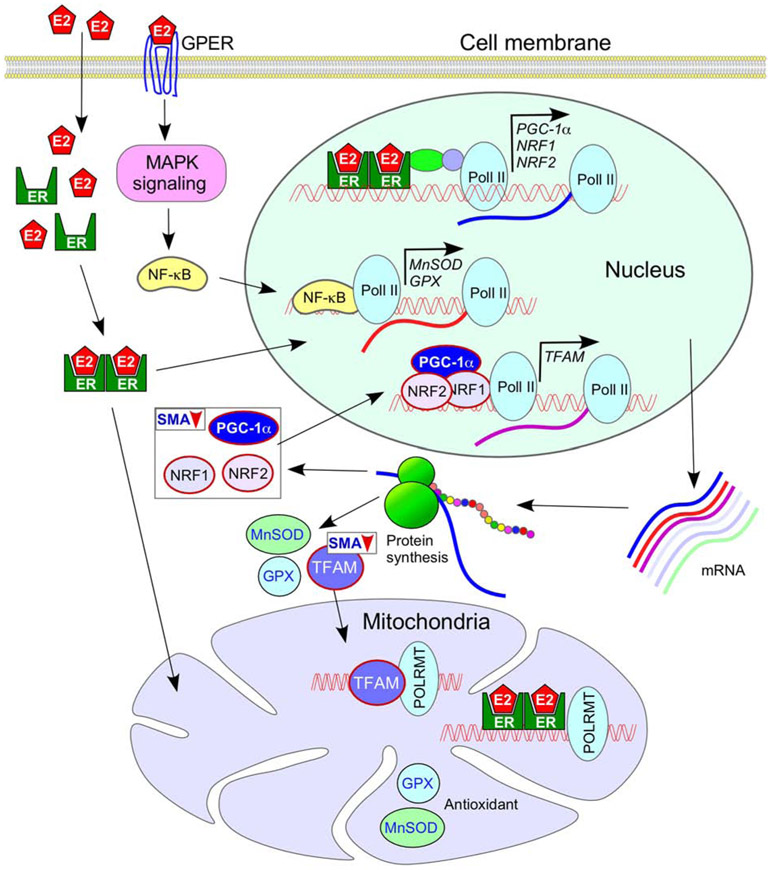
Figure 1.
Sex-specific effect of mitochondrial functions in tissues with high energy demand. Interactions of pol II and POLRMT with the nuclear and the mitochondrial DNA, respectively, have been shown. The female sex hormone estrogen (E2) regulates expression of transcription factors PGC-1α, NRF1 and NRF2 that are important for the expression of TFAM, a transcription factor. TFAM is essential for mitochondrial biogenesis. Both TFAM and E2 regulate expression of genes located on the mitochondrial genome. Through the MAPK signaling pathway, E2 also regulates expression of antioxidants GPX and MnSOD that localize to the mitochondria. PGC-1α, NRF1 and NRF2 are known to be downregulated in SMA, although it is not yet known if the downregulation is more pronounced in males. Details of pathways depicted here are described in the body of the main text and the accompanying references (see section 3). Abbreviations: E2, estrogen; ER, estrogen receptor; MnSOD, manganese superoxide dismutase; GPER, G protein-coupled estrogen receptor; GPX, glutathione peroxidase; MAPK, mitogen associated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NRF, nuclear respiratory factor; PGC-1α, Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha; pol II, RNA polymerase II; POLRMT, mitochondrial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase; TFAM, transcription factor A, mitochondrial.