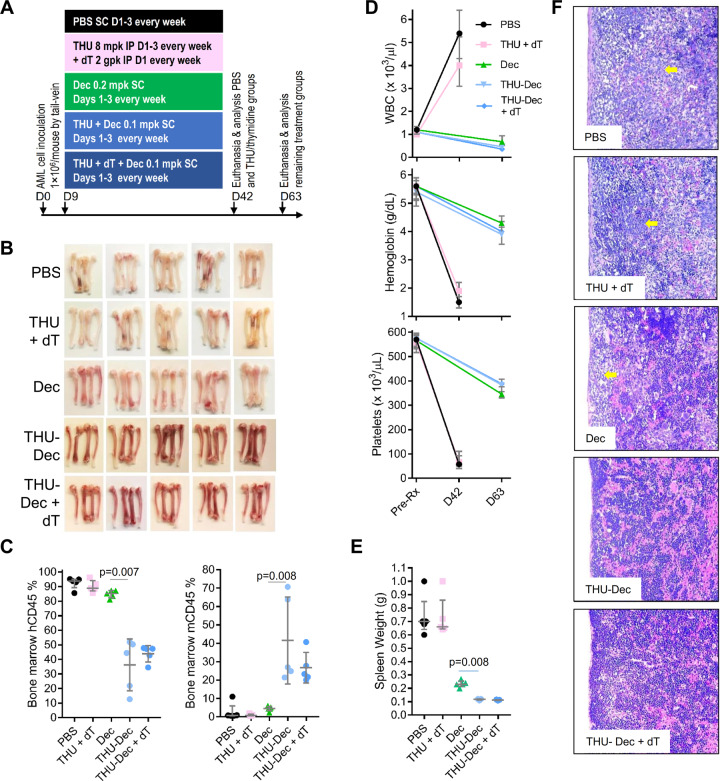
Fig. 4. Impact on efficacy of adding inhibitors of CDA and/or de novo pyrimidine synthesis.
NSG mice were tail-vein inoculated with patient-derived AML cells (1 × 106 cells/mouse) and randomized to (i) PBS vehicle; (ii) CDA-inhibitor (intra-peritoneal [IP] THU)+ de novo pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor (IP thymidine [dT]); (iii) Dec; (iv) THU + Dec; (v) THU + Dec + dT (n = 5/group). PBS and THU + dT mice were euthanized for distress on D42, and other mice were sacrificed for analysis on D63. a Experiment schema. b Femoral bones. White = leukemia replacement, reddish = functional hematopoiesis. c Bone marrow human (hCD45) and murine (mCd45) myelopoiesis content. Flow-cytometry. Median ± IQR. p value Mann–Whitney test two-sided. d Blood counts pretreatment and at euthanasia/sacrifice. Measured by Hemavet. Median ± IQR. e Spleen AML burden (spleen weights) at euthanasia/sacrifice. Median ± IQR. p value Mann–Whitney test two-sided. f Spleen histology. Hematoxylin-Eosin stain of paraffin-embedded sections. Magnification ×400. Leica DMR microscope.