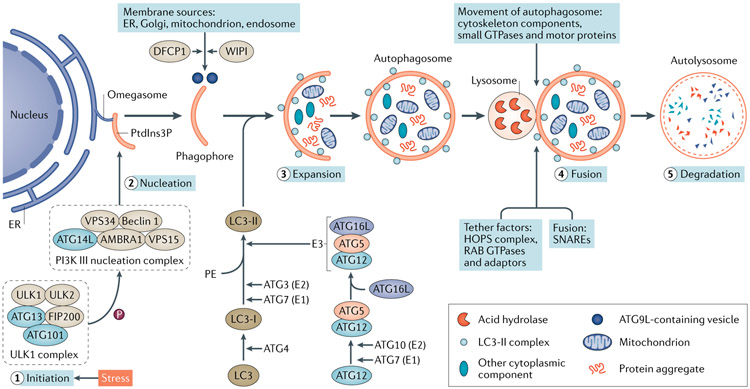
Fig. 1 ∣. Autophagy dynamics and core machinery.
Autophagy is a muitistep process involving initiation, nucleation, expansion, fusion and degradation. Upon induction, the ULK1 complex — comprising the serine/threonine protein kinases ULK1 and ULK2, autophagy-related protein 13 (ATG13), FAK family kinase-interacting protein of 200 kDa (FIP200) and ATG101 — phosphorylates multiple substrates, including components of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) III nucleation complex to promote phagophore nucleation. The PI3K III complex comprises PI3K catalytic subunit type 3 (VPS34), PI3K regulatory subunit 4 (VPS15), beclin 1, beclin 1-associated autophagy-related key regulator (ATG14L) and activating molecule in beclin 1-regulated autophagy protein 1 (AMBRA1). This complex produces phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate (PtdIns3P) at the omegasome, which recruits PtdIns3P-binding proteins for phagophore expansion. The delivery of membrane from other sources to the expanding phagophore requires PtdIns3P-binding proteins WD repeat domain phosphoinositide-interacting proteins (WIPIs) and zinc-finger FYVE domain-containing protein 1 (DFCP1), as well as cycling of the transmembrane protein ATG9L in the form of membrane vesicles and tubules. Two ubiquitin-like conjugation systems, the ATG12–ATG5–ATG16L system and the microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3) system, participate in autophagosome elongation and completion. The conversion of cytosolic LC3-I into membrane-bound LC3-II is indicative of autophagy induction and autophagosome formation. The completed autophagosome then fuses with a lysosome to form an autolysosome, in which the autophagosome inner membrane and cargos are degraded by lysosomal hydrolases and eventually released for recycling. The fusion process is regulated by a large set of molecules, including cytoskeleton components and related motor proteins, tethering factors including the homotypic fusion and vacuole protein sorting (HOPS) complex, the RAB GTPases, and specific soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complexes. E1, ubiquitin-activating enzyme; E2, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme; E3, ubiquitin ligase; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine.