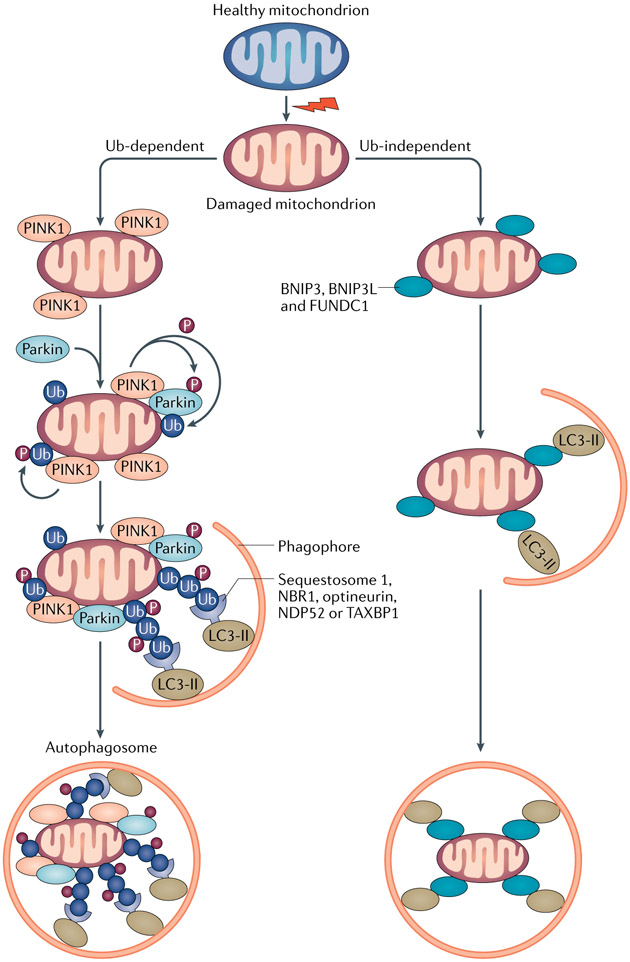
Fig. 2 ∣. Mitophagy pathways and cargo recognition.
Mitophagy is mainly mediated by microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 (LC3)-associated autophagy receptors via both ubiquitin (Ub)-dependent and Ub-independent pathways. Ub-dependent mitophagy involves the mitochondrial serine/threonine protein kinase PINK1 and E3 Ub-protein ligase parkin (PINK1–parkin) pathway. Following loss of mitochondrial membrane potential, PINK1 accumulates on the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), where it recruits and phosphorylates parkin to add phospho–Ub chains on OMM proteins. Autophagy receptors, such as sequestosome 1, next to BRCA1 protein (NBR1), optineurin, calcium-binding and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 2 (NDP52) and TAX1-binding protein 1 (TAX1BP1), which contain both Ub-binding domains and LC3-interacting regions (LIRs), bridge the ubiquitylated mitochondria to LC3-associated autophagosomal membranes for sequestration. PINK1-mediated phosphorylation of ubiquitin might be sufficient to recruit NDP52 and optineurin and induce mitophagy independently of parkin. Ub-independent mitophagy is mediated by several OMM receptors such as BCL-2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3 (BNIP3), BNIP3-like (BNIP3L), FUN14 domain-containing protein 1 (FUNDC1), which do not require interaction with Ub for cargo recognition. Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP8 and BCL-2-like 13 (BCL2L13) are potential additional mitophagy receptors. By binding to LC3 via the LIRs at their cytosolic N terminus, mitophagy receptors link damaged mitochondria directly to autophagosomes.