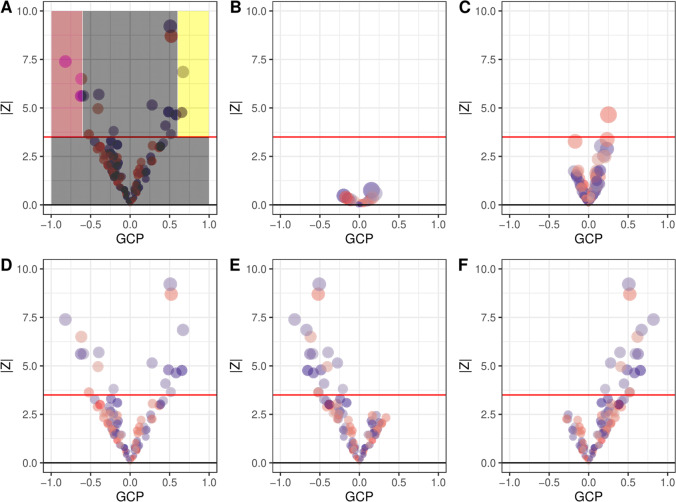
Fig. 2. Interpretation of causal architecture plots.
Each panel represents phenome-wide LCV scan of a target trait (trait A), against each of hundreds anchor traits (trait B). Each dot represents a target trait tested against an anchor trait and the red line represents the statistical significance threshold (FDR < 5%). The size of each dot is proportional to GCP z-score, blue dots correspond to traits with positive genetic correlation (rG), while red dots correspond to traits with negative rG. a Schematic showing regions of the plot which represent noncausal relationships (gray), upstream (pink), and downstream (yellow) causal relationships, b Underpowered experiment, c well-powered experiment for a trait with limited causal relevance, d the trait has many causal relationships in both upstream and downstream directions, e a trait which is causally affected by other upstream traits, f a trait with downstream effects. (Color figure online).