Figure 2.
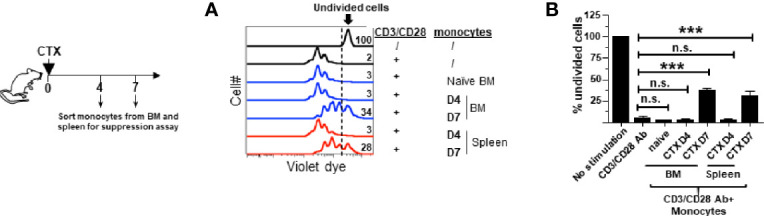
Monocytes in the spleens and bone marrows acquire suppressive activity after CTX treatment. Following the timeline depicted in the schema, naïve Balb/c mice were treated with CTX. At the indicated time points (day 4 and 7 after CTX treatment), spleens and bone marrows were collected and stained for CD11b and Ly6C. Monocytes (CD11b+Ly6Chi) and neutrophils (CD11b+Ly6Clo) were flow-sorted for in vitro T-cell suppression assay. Monocytes from the BM of untreated naïve mice were included as a control. Spleen cells from naïve Balb/c were labeled with violet dye, and the T cells within the splenocytes served as responder cells. Responder cells were mixed with equal numbers of sorted myeloid cells and stimulated with aCD3/aCD28 mAbs. After 3 days in culture, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) The proliferation of responder T cells was evaluated by violet dye dilution. The numbers in the histogram overlay indicate the percentage of undivided cells under each condition. (B) The frequencies of undivided responder T cells under each culture condition are summarized in bar graph and shown as mean ± SD of triplicate cultures. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments. n.s. not significant, ***p < 0.001.
