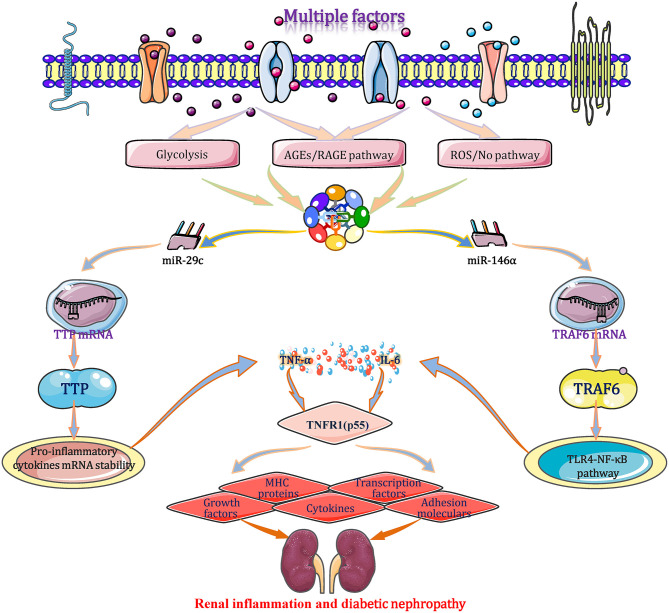
Figure 7.
miRNAs interfere with inflammation and immune in DN by affecting TNF-α expression. Under a diabetic state, the expression level of TNF-α is regulated by miRNAs (such as miR-29c, 146a, and miR-31) through several signaling pathways. TNF-α binds to the TNFR1 (p55) receptor, resulting in the production/expression of diverse effectors include adhesion molecules, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins, cytokines, growth factors, transcription factors (TFs) and acute phase proteins, leading to direct renal cell cytotoxicity, apoptosis, intraglomerular haemodynamic alterations, and renal immune/inflammation responses. These alterations play important roles in the courses of inflammatory and immune in DN and may be exploited as potential therapeutic strategies for DN based on the miRNA targets. MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; TNFR1, tumor necrosis factor-α receptor 1; TTP, tristetraprolin; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6.