Figure 1.
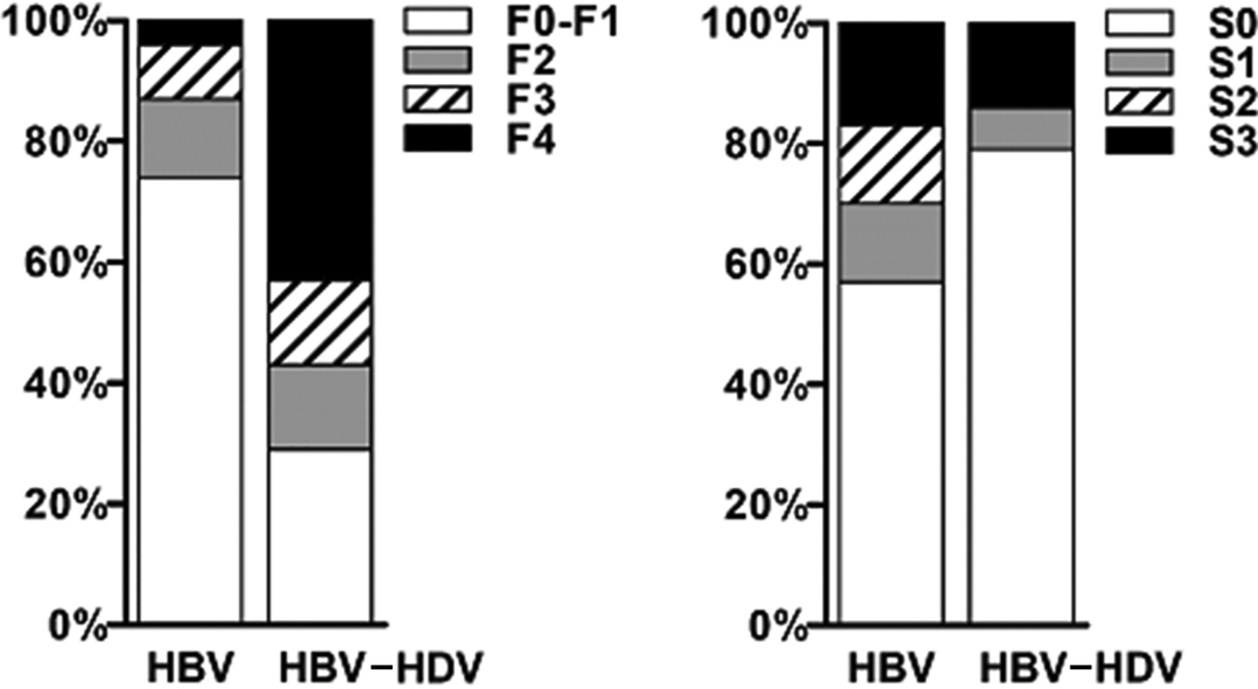
Assessment of liver fibrosis and steatosis in HBV mono- vs HBV/HDV super-infected patients. HBV mono- (n=23) and HBV/HDV super-infected (n=14) patients underwent the assessment of the degree of liver fibrosis (left) and steatosis (right) via controlled transient elastography (FibroScan®, Echosens, Paris, France) and controlled attenuation parameter (CAP®, EchoSens, Paris, France), respectively. HBV/HDV super-infected patients had more fibrosis compared to HBV mono-infected patients (p=0.01052). There was no difference in steatosis grades (p=NS). F0-F1: none to mild fibrosis; F2: moderate fibrosis; F3: severe fibrosis; F4: cirrhosis. S0: no steatosis; S1: mild steatosis; S2: moderate steatosis; S3: severe steatosis.
