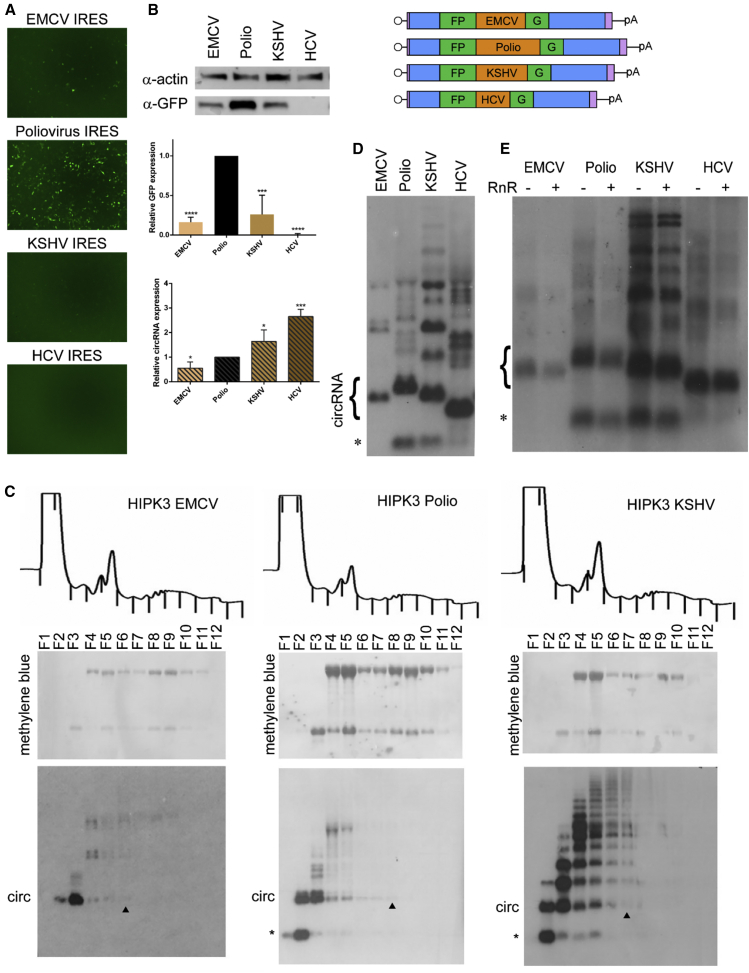
Figure 3.
IRES elements affect translation efficiency and circRNA expression levels
The HIPK3 split GFP construct was created with either the EMCV, Polio, KSHV vFLIP, or HCV IRES elements. (A and B) Constructs were transfected into HEK293 cells and expression assayed at 4 days post-transfection by (A) GFP fluorescence and (B) western blot analysis, with actin as a loading control (quantification below). (C) To assay translation efficiency, the indicated constructs were transfected into HEK293 cells and harvested in cycloheximide followed by a sucrose gradient and fractionation. Top: OD trace of the gradient, with fractions marked by lines. Middle: RNA was extracted from gradients, separated by gel electrophoresis, transferred to a membrane, and stained with methylene blue to visualize the ribosomal RNA. Bottom: the same membrane was probed for GFP sequences. The arrowhead marks the last fraction in which the circRNA is detected. (D) RNA from transfected cells was assayed by northern blot and probed for GFP sequences (quantification left). (E) RNA was digested by RNase R (RnR) followed by northern blotting, probing for GFP sequences. On northern blots, the asterisk refers to an additional circular band. Western and northern blots were quantified as detailed in Materials and methods and graphed relative to the unchanged HIPK3 intron construct. Student’s t test was performed to test for statistical significance. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.005; ∗∗∗p < 0.0005; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.00005.