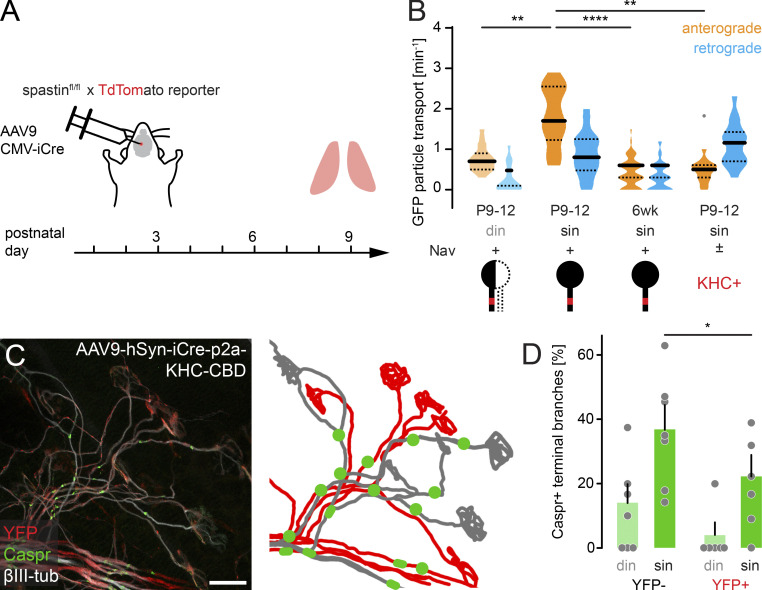
Figure 5.
Axonal transport limits myelination onset in terminal motor axon branches. (A) Schematic of experimental design. AAV9-hSyn-iCre-p2a-KHC-CBD was injected at P2 into the third ventricle of YFP reporter mice. Muscles were analyzed at P9. (B) Quantification of axonal GFP particle transport in β1-Nav-GFP animals (n ≥ 5 mice per group, n ≥ 16 axons). (C) Image of AAV9-hSyn-iCre-p2a-KHC-CBD-injected P9 triangularis sterni muscle of a YFP reporter mouse immunostained for Caspr (green) and βIII-tubulin (white). KHC-CBD is overexpressed in iCre-induced recombined YFP reporter–positive axons (red). Schematic on the right depicts YFP-positive (red) and YFP-negative motor units (gray) and Caspr paranodes (green). (D) Quantification of Caspr immunostaining on YFP-negative and YFP-positive terminal axon branches at P9 (n ≥ 5 mice per group, n ≥ 39 axons per mouse). din, competing axons; sin, winner axons. Data represent mean + SEM. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; Mann–Whitney test. Outlier determined by Tukey test. Scale bar, 20 µm (C).