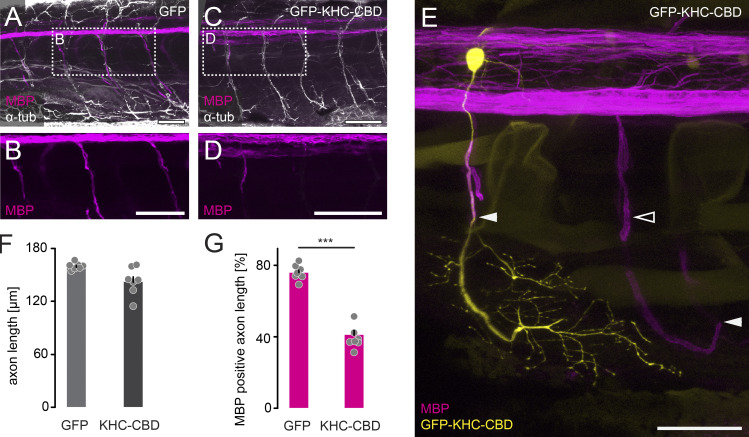
Figure S4.
Microtubule-dependent axonal transport affects myelination onset. (A–D) Whole-mount immunohistochemical staining against α-tub (white) to label axons in Tg(mbp:RFP) (magenta) transgenic zebrafish larvae injected with cntn1b:GFP as control (A and B) and cntn1b:GFP-KHC-CBD (C and D). Dashed boxes in A and C are enlarged in B and D showing mbp:RFP only. (E) Example of an individual cntn1b:GFP-KHC-CBD–labeled motor neuron (yellow) and its myelination (magenta). Solid arrowheads point to ends of myelin sheaths; empty arrowhead points to extend of myelination along KHC-CBD–expressing axons compared with control axons in the adjacent somite (unlabeled). (F) Length of spinal motor axons, measured between the branching-off point at the spinal cord to the axon tip (n = 7 zebrafish per group, n ≥ 29 axons per animal). (G) Progress of myelination expressed as percentage of mbp:RFP-positive axon length (n = 7 zebrafish per group, n ≥ 29 axons per animal). Data represent mean + SEM. ***, P < 0.001, Mann–Whitney test. Scale bar, 50 µm (A–E).