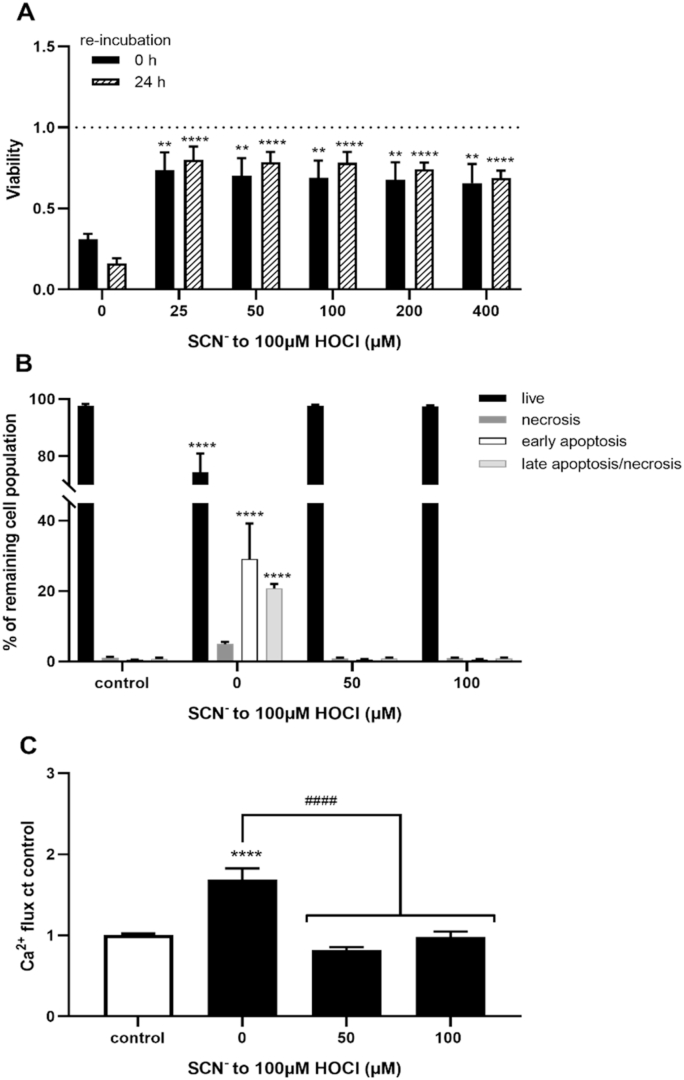
Fig. 1.
Prevention of HOCl-induced cell death and intracellular Ca2+accumulation by SCN−. HCASMC were exposed to 100 μM HOCl with addition of increasing concentrations of SCN− for 15 min. (A) The changes in metabolic activity were assessed by MTS assay directly after treatment (black bars) and after treatment with re-incubation for 24 h in growth media (dashed bars) and expressed as a fold change compared to control cells. Data in (B) show the cell populations 24 h post-treatment, following a washing step which removes any non-adherent, dead cells resulting from the initial HOCl exposure, assessed using APC Annexin V/PI cell death kit and flow cytometry analysis. Percentage of live cell population (A-/PI-, black bars), of necrotic (A-/PI+, dark grey bars), early apoptotic (A+/PI-, white bar) and late apoptotic/necrotic (A+/PI+, light grey bar) cell populations. (C) Accumulation of intracellular Ca2+ in HCASMC immediately after the treatment with flow cytometry and staining with Fluo-4AM. Data represent the geometric means as a fold change compared to control. Statistical significance indicated by **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001, ####p < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc testing. In (A) the asterisks indicate significance compared to HOCl treatment alone, in (B–C) asterisks indicate significance compared to the non-treated control, and # indicates significance compared to the HOCl treatment.