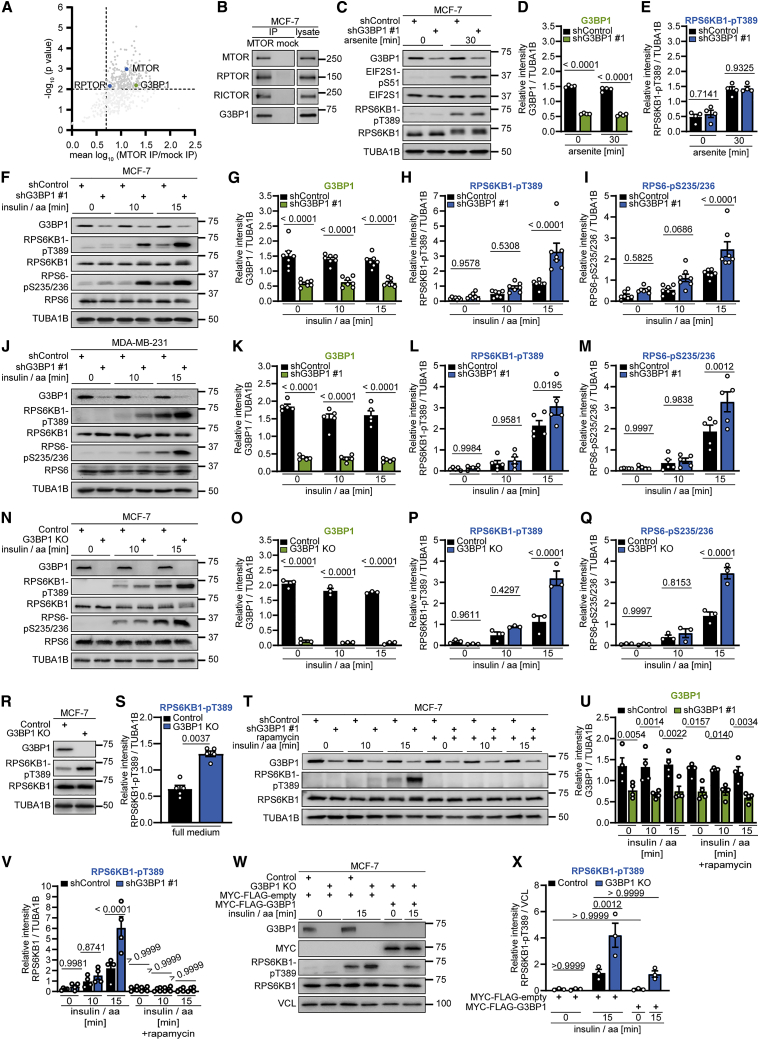
Figure 1.
G3BP1 suppresses mTORC1 activation by insulin and nutrients
(A) Re-analysis of the MTOR interactome (Schwarz et al., 2015). Shown are mean log10 ratios of proteins in MTOR versus mock IP.
(B) IP against MTOR or mock (rat immunoglobulin G [IgG]). n = 6.
(C) Arsenite-treated shG3BP1 #1 cells. n = 4.
(D) Quantitation of G3BP1 in (C). Shown are data points and mean ± SEM.
(E) Quantitation of RPS6KB1-pT389 in (C). Data are shown as in (D).
(F) Insulin and amino acid (insulin/aa)-stimulated shG3BP1 #1 cells. n = 7.
(G) Quantitation of G3BP1 in (F). Shown are data points and mean ± SEM.
(H) Quantitation of RPS6KB1-pT389 in (F). Data are shown as in (G).
(I) Quantitation of RPS6-pS235/236 in (F). Data are shown as in (G).
(J) Insulin/aa-stimulated shG3BP1 #1 cells. n = 5.
(K) Quantitation of G3BP1 in (J). Shown are data points and mean ± SEM.
(L) Quantitation of RPS6KB1-pT389 in (J). Data are shown as in (K).
(M) Quantitation of RPS6-pS235/236 in (J). Data are shown as in (K).
(N) Insulin/aa-stimulated G3BP1 KO cells. n = 3.
(O) Quantitation of G3BP1 in (N). Shown are data points and mean ± SEM.
(P) Quantitation of RPS6KB1-pT389 in (N). Data are shown as in (O).
(Q) Quantitation of RPS6-pS235/236 in (N). Data are shown as in (O).
(R) Full-medium-cultured G3BP1 KO cells. n = 5.
(S) Quantitation of RPS6KB1-pT389 in (R). Shown are data points and mean ± SEM.
(T) Rapamycin treatment of insulin/aa-stimulated shG3BP1 #1 cells. n = 4.
(U) Quantitation of G3BP1 in (T). Shown are data points and mean ± SEM.
(V) Quantitation of RPS6KB1-pT389 in (T). Data are shown as in (U).
(W) Insulin/aa-stimulated G3BP1 KO cells transfected with MYC-FLAG-G3BP1 (48 h). n = 3.
(X) Quantitation of RPS6KB1-pT389 in (W). Shown are data points and mean ± SEM.
See also Figures S1 and S2 and Table S1.