Figure 7.
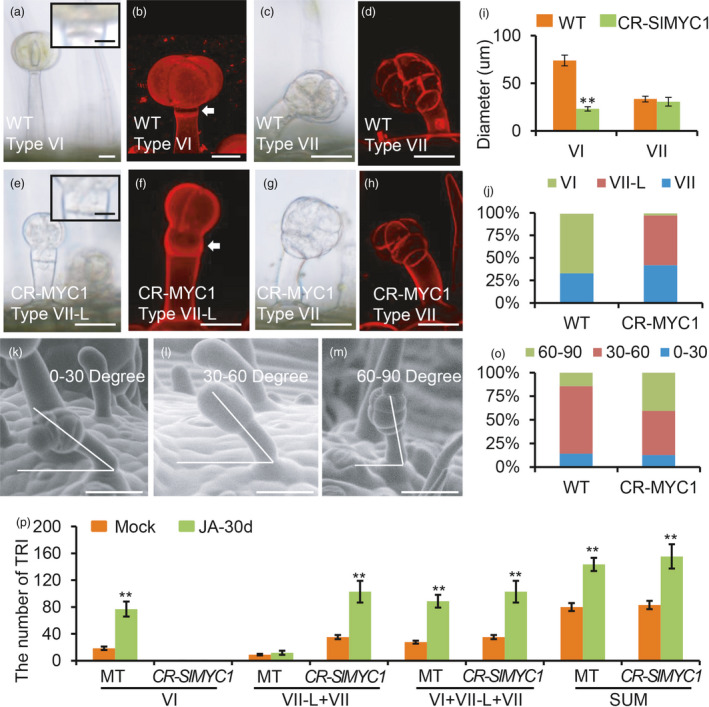
SlMYC1 regulates the morphology of type VI trichomes. (a‐h) The morphology of the type VI, VII and VII‐Like (VII‐L) trichomes in WT and CR‐MYC1 plants under DIC (a, c, e, g) and confocal microscope (b, d, f, h). The upper right insets in the Figure a and e show the close‐up view of the intermediate cell of type VI trichomes. Scale bar: 10 μm. The white arrows in the Figure b and f point to the intermediate cells. Trichomes were stained with propidium iodide (PI) in the Figure b, d, h and f. Scale bar: 25 μm. (i) The diameter of the glandular cells of type VI and VII trichomes in WT and CR‐MYC1 plants. Values are represented as means ± SD (n = 100). Asterisks indicate significant differences by t‐test: **P < 0.01, *0.01 < P < 0.05. (j) The percentage of the type VI, VII‐L and VII trichomes in WT and CR‐MYC1 plants based on the morphology of the glandular cells. Three independent lines of CR‐SlMYC1 plants were measured. (k–m) The curvature of type VII trichomes in the WT. The curvature is 0‐30 degree (k), 30–60 degree (l) and 60–90 degree (m) relative to the leaf surface. The images were taken by SEM. Scale bar: 30 μm. (o) The percentage of the small glandular trichomes with different curvatures in WT and CR‐MYC1 plants. Three independent lines of CR‐SlMYC1 were measured. (p) The number of the trichomes on the leaf of WT and CR‐SlMYC1 plants with MeJA treatment. ‘SUM’ on the X‐axis means the sum of all types of trichomes. Values are represented as means ± SD (n = 10). Asterisks indicate significant differences by t‐test: **P < 0.01, *0.01 < P < 0.05. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
