Figure 1.
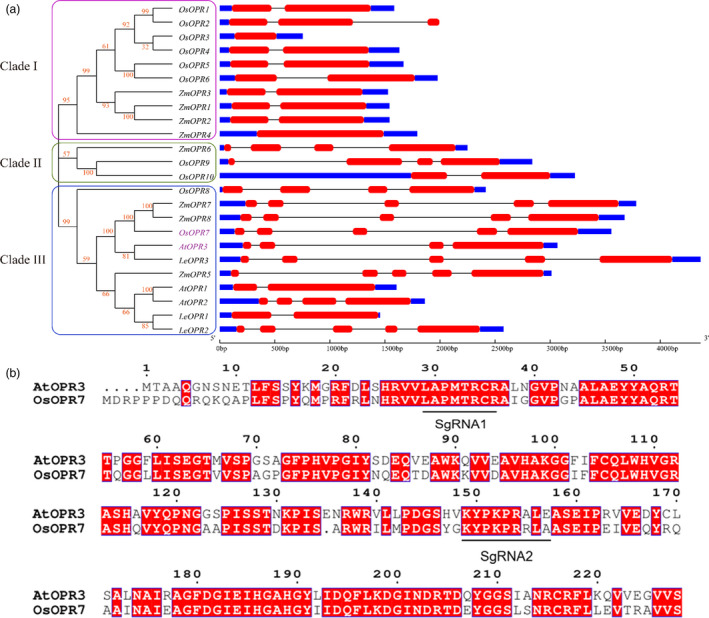
Orthologous OPRs across species. (a) Phylogenetic tree and gene structures of OPRs from various species. Clades I, II and III are indicated in fuchsia, green and light blue lines, respectively. The constructed maximum‐likelihood tree, built using the ClustalW program with 1000 bootstrap replicates, is based on the alignment of 24 OPR coding sequences. The digits in red stand for the bootstrap values. AtOPR3 and OsOPR7 are indicated with purple colour. The right side of the figure displays the gene structures of OPRs from Arabidopsis thaliana (At), Oryza sativa (Os), Zea mays (Zm) and Solanum lycopersicum (Le), which are in the order of their appearance in the phylogenetic tree. Coding sequences (CDS) and untranslated regions (UTR) are shown in the red and blue boxes, respectively. Introns are indicated with horizontal lines. (b) Comparison of the encoded amino acid sequences between AtOPR3 and OsOPR7. The red colour boxes show the amino acids present in the two genes. The underlines indicate the SgRNAs designed. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
