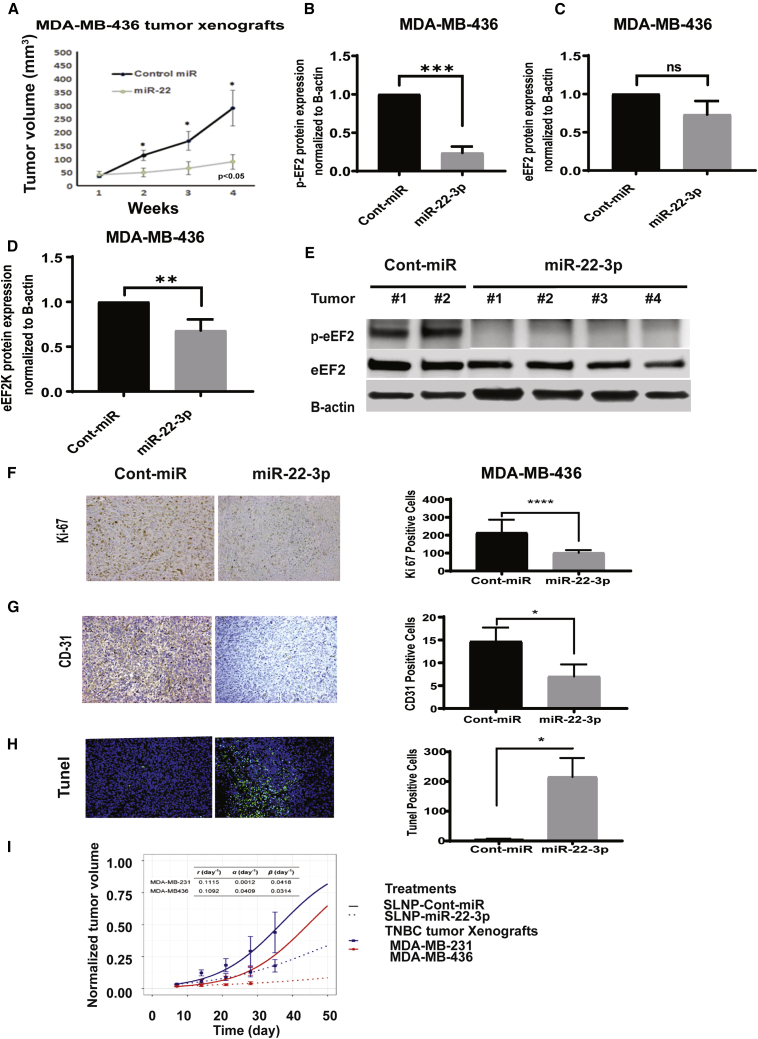
Figure 8.
Systemic administration of SLNP-miR-22-3p inhibits the growth of MDA-MB-436 TNBC xenografts in nude mice
(A) MDA-MB-436 TNBC cells were orthotopically injected into the mammary fat pads of female athymic nude mice. The mice were randomized to two treatment groups: SLNP-miR-22-3p or SLNP-control miRNA (0.15 mg/kg administered intravenously twice a week for 4 weeks; five mice/group). MDA-MB-436 tumor xenograft volumes were measured weekly. (B−E) Western blot analyses of p-eEF2 (B), eEF2 (C), and eEF2K (D) protein levels in MDA-MB-436 tumors. ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (F and G) Immunohistochemistry analysis of Ki-67 (F) and CD31 (G) in MDA-MB-436 tumor xenograft after SLNP-miR22-3p or control-miRNA treatments. (H) TUNEL assay showing apoptotic cells (green) in tumors after SLNP-miR22-3p or SLNP-control miRNA in an MDA-MB-436 orthotopic model. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. (I) A mathematical model was applied to evaluate the in vivo antitumor efficacy of treatment with miR-22-3p in the MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 TNBC orthotopic xenograft mouse models. Tumor growth rates (r) were first estimated for MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-436 cells (solid lines), and their tumor growth-inhibition (α) and decay (β) rates were estimated under treatment with miR-22-3p nanoparticles (dashed lines). Estimated parameter values are shown at the top of the graph.