FIGURE 2.
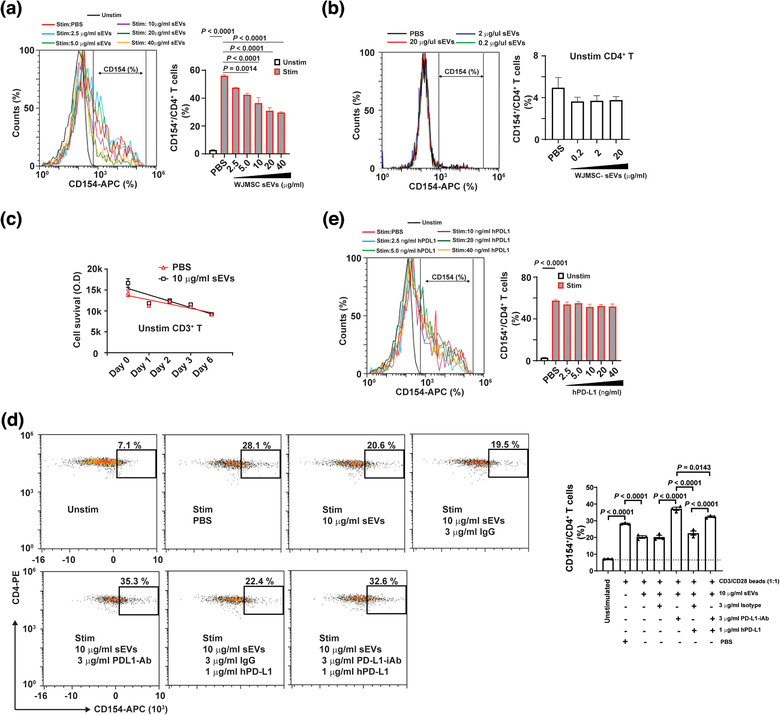
WJMSC sEVs inhibit TCR‐mediated CD4+ TCA through PD‐L1. (a) Flow cytometry showing the inhibitory effects of WJMSC‐derived sEVs on CD4+ T cell activation (CD154+) in a dose‐dependent manner (left) and quantitative analysis (right). (b) Effects of WJMSC sEVs on unstimulated CD4+ T cells (left) and quantitative analysis (right), measured by flow cytometry. (c) Survival of unstimulated CD3+ T cells treated with PBS or 10 µg/ml WJMSC sEVs for 6 days. (d) Representative flow charts (left) and quantitative analysis (right) of activated CD4+ T cells incubated with 10 µg/ml WJMSC sEVs, 3 µg/ml PD‐L1‐iAb/isotype, or 1 µg/ml hPD‐L1 for overnight. (e) Flow cytometry showing the effects of soluble hPD‐L1 on activated CD4+ T cells (left) and quantitative analysis (right). Peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC)s were stimulated with (Unstim) or without (Stim) CD3/CD28 Dynabead at a dilution of 1:1 ratio (a,d,e). hPD‐L1, recombinant human PD‐L1 (d,e). PD‐L1‐iAb, neutralization antibody for human PD‐L1 (d). Data are mean ± s.e.m (n = 3) and analysed by one‐way ANOVA (a,b,d,e). Experiments independently repeated three times (a,d,e)
