Figure 1.
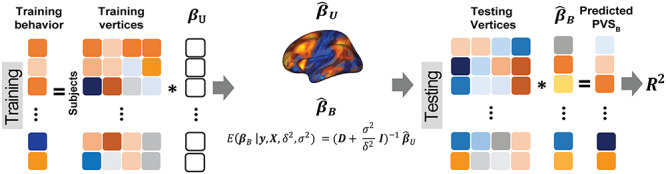
Overview of the PVSB and the PVSU algorithms. Ten-fold cross-validation was performed to obtain a PVSB for each individual. For each fold, mass univariate summary statistics, 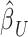 , were obtained from the training set which contained 90% of the complete sample. Posterior mean effect sizes at each vertex,
, were obtained from the training set which contained 90% of the complete sample. Posterior mean effect sizes at each vertex, 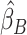 , were approximated by multiplying the mass univariate beta estimates,
, were approximated by multiplying the mass univariate beta estimates, 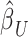 , by the inverse of the correlation structure of the brain, D, and a shrinkage factor that accounts for the number of vertices, V, and the total signal of the brain-behavior association. The PVSB was subsequently calculated for the test set participants by multiplying their imaging phenotype with the
, by the inverse of the correlation structure of the brain, D, and a shrinkage factor that accounts for the number of vertices, V, and the total signal of the brain-behavior association. The PVSB was subsequently calculated for the test set participants by multiplying their imaging phenotype with the 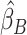 . Simulations were conducted at three levels of total explainable signal, six levels of study sample size, and four levels of proportion of non-null vertices, yielding 60 instantiations of simulation conditions with 100 iterations per condition.
. Simulations were conducted at three levels of total explainable signal, six levels of study sample size, and four levels of proportion of non-null vertices, yielding 60 instantiations of simulation conditions with 100 iterations per condition.
