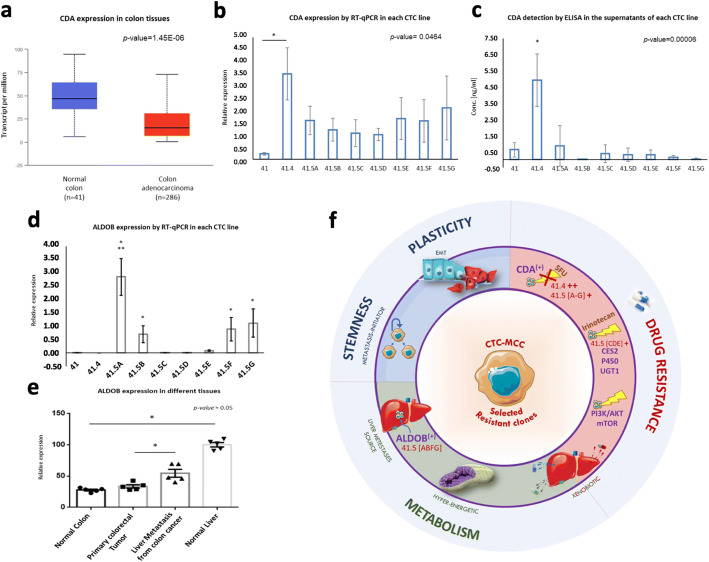
Fig. 2.
Major features of the aggressive colon cancer CTC clones selected after treatment. a Boxplot showing cytidine deaminase (CDA) relative expression in normal colon (n = 41) and colon adenocarcinoma (n = 286) samples using UALCAN (p-value = 1.45E-06). b RT-qPCR analysis of CDA gene expression in the nine CTC lines (mean values of triplicate experiments with standard deviation). c ELISA measurement of CDA protein level (ng/ml) in the conditioned medium from the nine CTC lines (mean values from triplicate experiments with standard deviation). Aldolase B (ALDOB) expression analysis (d) by RT-qPCR in the nine CTC lines [*significant upregulation in the CTC-MCC-41.5 [ABFG] cell lines compared with all the other CTC lines (p-value = 0.0134), and only with the CTC-MCC-41.5 [CDE] lines (p-value = 0.0466); **significantly upregulation compared with all the other CTC lines (p-value = 0.0017)], and e in tissue samples (normal colon, normal liver, primary colorectal tumor, liver metastases of colon cancer) (n = 5/tissue). f Representation of the cancer hallmarks of the CTC lines resistant to treatment: (i) Stemness and Plasticity: metastasis-competent potential, (ii) Drug resistance: different molecules and pathways involved in treatment resistance and drug detoxification, such as the CDA enzyme implicated in pyrimidine analogue metabolism (e.g. for 5-FU), (iii) Metabolism: xenobiotic metabolism linked to therapy resistance, energy metabolism linked to mitochondrial activity, and ALDOB activity that gave information also on the liver metastasis origin of the CTC41.5[ABFG] lines. Abbreviation: EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition