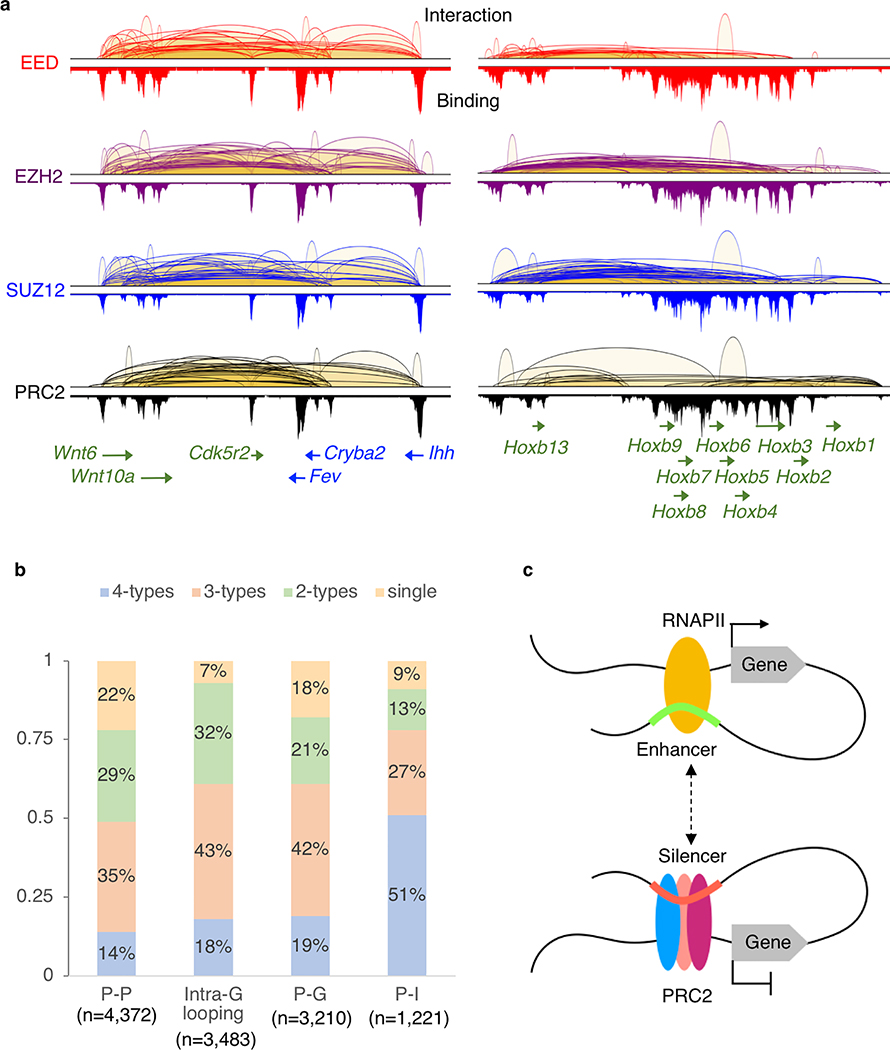
Extended Data Fig. 2: Extensive chromatin interactions between DREs and PRC2 bound genes.
a. Examples of the multiple co-occurred chromatin looping patterns (P-P, P-G, P-I and intra-G interactions) in the Wnt6-Ihh (chr1:74,751,523–74,968,999) and Hoxb (chr11:96,161,617–96,425,610) regions are shown from EED (red), EZH2 (purple), SUZ12 (blue) and PRC2 (black) ChIA-PET libraries, respectively. b. Percentages of genes exhibit single, 2-type, 3-type and all 4-type of interactions. For example, among the 4,372 genes with P-P interactions, 14% of them have all 4-type of interactions (P-P, P-I, P-G and intra-G looping). c. Proposed model on how DREs can connect to their target genes and function as either enhancers or silencers by binding to RNAPII or PRC2.