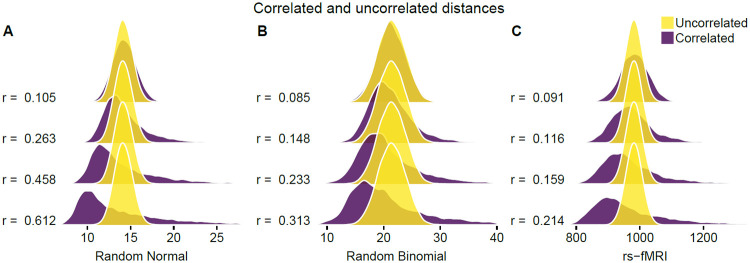
Fig 12. Distance densities from uncorrelated vs correlated bioinformatics data.
(A) Euclidean distance densities for random normal data with and without correlation. Correlated data was created by multiplying random normal data by upper-triangular Cholesky factor from randomly generated correlation matrix. We created correlated data for average absolute pairwise correlation (Eq 176) . (B) TiTv distance densities for random binomial data with and without correlation. Correlated data was created by first generating correlated standard normal data using the Cholesky method from (A). Then we applied the standard normal CDF to create correlated uniformly distributed data, which was then transformed by the inverse binomial CDF with n = 2 trials and success probabilites . (C) Time series correlation-based distance densities for random rs-fMRI data (Fig 9) with and without additional pairwise feature correlation. Correlation was added to the transformed rs-fMRI data matrix (Fig 9) using the Cholesky algorithm from (A).