Fig. 5.
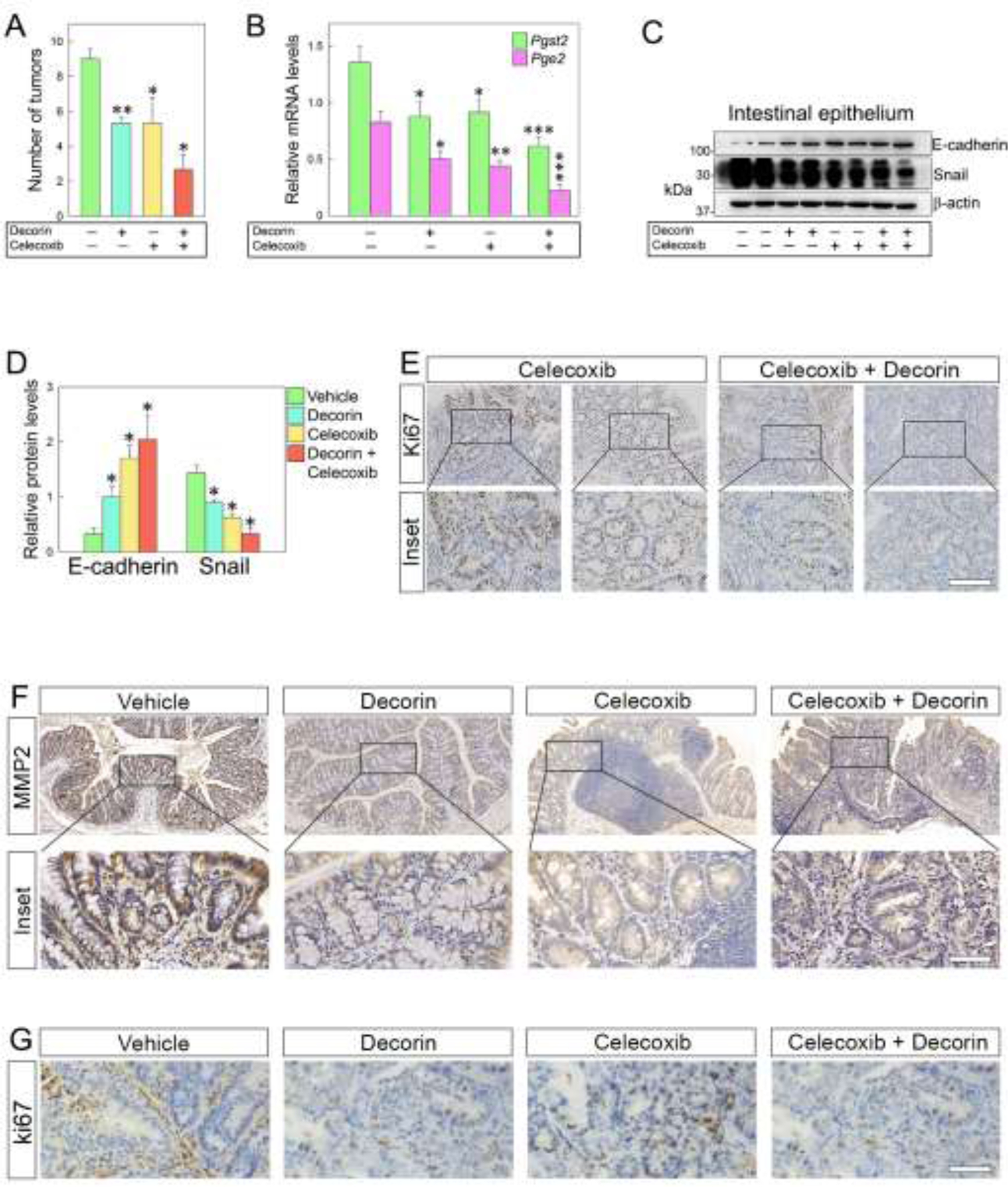
Combined treatment with decorin and Celecoxib significantly inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition and proliferation of colorectal cancer cells in Dcn−/− mice. (A) Tumor numbers of mice bearing tumors and treated with decorin, Celecoxib, or both. Mice treated with both therapeutic agents show a ~70% reduction in the number of tumors compared to the vehicle-treated group. (B) Relative mRNA levels of Ptgs2 and Pge2 in the neoplastic intestinal epithelium following treatment with decorin and Celecoxib. (C) Western blots showing E-cadherin and Snail levels in intestinal epithelial cells after treatment with decorin, Celecoxib, or both, and (D) relative quantification. (E) Immuno-histochemical detection of the proliferative marker Ki67 in Dcn−/− mice at 12 weeks after AOM/DSS induction. (F-G) Immuno-histochemical detection of MMP2 and Ki67 respectively in the mouse intestinal epithelium following combined treatment with decorin and Celecoxib. The experiments were performed in triplicate. Data are expressed as mean ±S.D. *p< 0.05, **p0.01, **p< 0.001.
