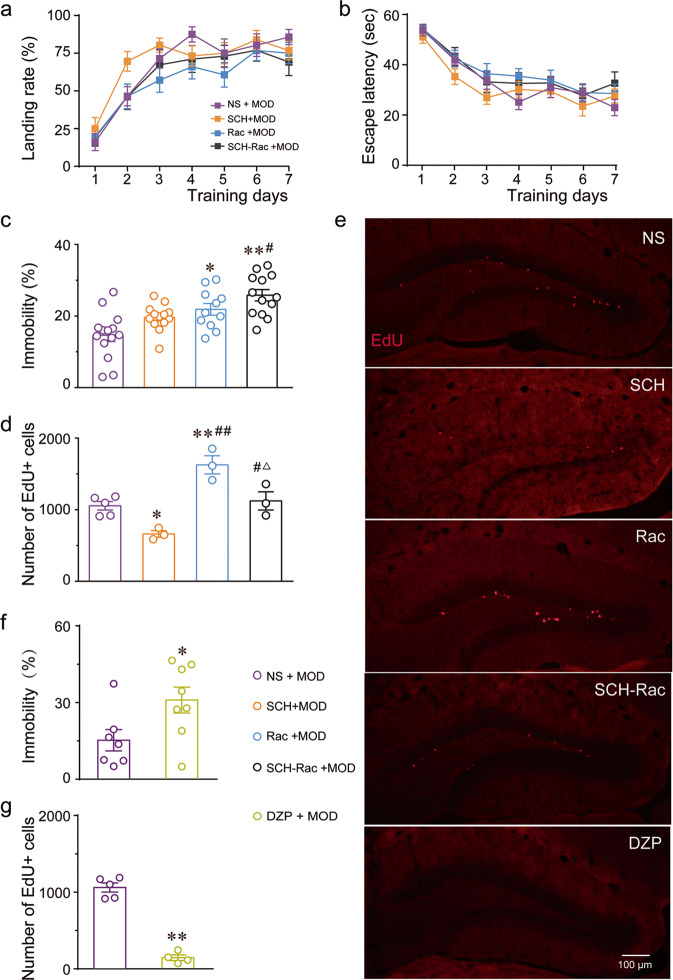
Fig. 5. Dopamine and GABAA receptors mediate MOD-produced anti-depressant effects and hippocampal neurogenesis-promotion in ovariectomized mice.
a–d In ovariectomized mice treated with modafinil (MOD) at 45 mg/kg in the presence of saline (NS), a selective D1 receptor antagonist SCH23390 (SCH), a selective D2 receptor antagonist raclopride (Rac), and combined use of SCH and Rac, respectively, the landing rates (a) and escape latencies (b) locating the invisible platform during the seven training days in the Morris water-maze test (NS, SCH, Rac: n = 14 per group; SCH–Rac: n = 13), percentage of immobility time in the forced swimming test (FST) (c) (NS: n = 14; SCH, SCH–Rac: n = 13 per group; Rac: n = 11), and the numbers of newborn hippocampal neurons (d) (NS: n = 5; SCH, Rac, and SCH-Rac: n = 3 per group). e Representative images of EdU staining in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in each group of mice with ovariectomy (OVX). f, g In OVX mice treated with MOD in the presence of NS or a selective GABAA receptor agonist diazepam (DZP), the percentage of immobility time in the FST (f) (NS: n = 7; DZP: n = 8) and the numbers of newborn hippocampal neurons (g) (NS: n = 5; DZP: n = 4). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus NS group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01 versus SCH group; △p < 0.05 versus Rac group. EdU 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine.