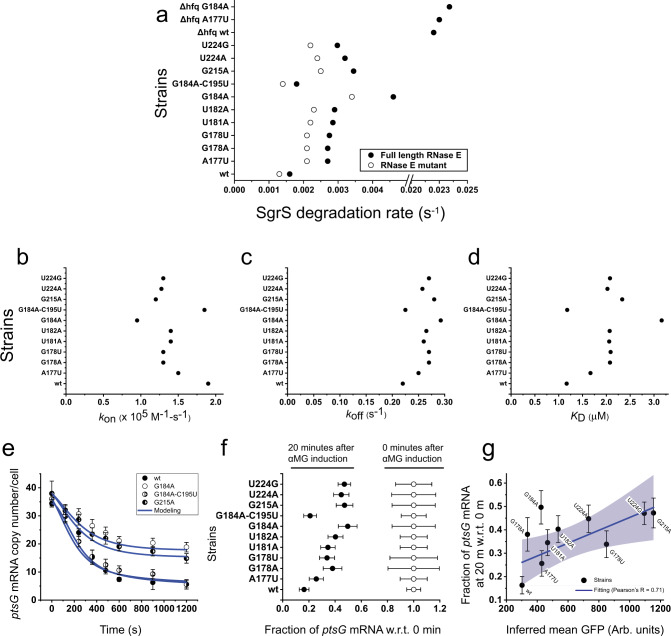
Fig. 6. Calculation of various parameters and correlation with Sort-Seq.
a Degradation rates of SgrS for the wild type and the strains A177U, G178A, G178U, U181A, U182A, G184A, G184A–C195U, G215A, U224A, U224G, ∆hfq wild type, ∆hfq A177U, and ∆hfq G184A for full-length RNase E and RNase E mutants. Error bars represent standard deviation from two experimental replicates. b–d kon, koff, and KD measured from the time-dependent modeling curves of the SgrS, ptsG mRNA, and SgrS-ptsG mRNA complexes for the wild type and strains A177U, G178A, G178U, U181A, U182A, G184A, G184A–C195U, G215A, U224A, and U224G. These were determined simultaneously in the wild-type and RNase E mutants. Error bars report standard deviation from the independent fitting on two replicates. e Time course changes in ptsG mRNA for the wild type, G184A, G184A–C195U, and G215A mutant strains. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM from n = 98, 90, 169, 144, 149, 127, 94, and 82 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 min induction, respectively, for wild type; for n = 84, 84, 94, 99, 94, 90, 87, and 88 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 min induction, respectively, for G184A mutant strain; for n = 117, 101, 115, 111, 102, 110, 104, and 104 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 min induction, respectively, for G184A–C195U mutant strain and for n = 82, 88, 94, 104, 94, 90, 89, and 88 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 15, and 20 min induction, respectively, for G215A mutant strain. f Fractional change in ptsG mRNA copy numbers for the wild type and the mutants A177U, G178A, G178U, U181A, U182A, G184A, G184A–C195U, G215A, U224A, and U224G before and after 20 min αMG induction. Data are presented as mean values ± SEM from n = 98 and 82 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for wild type; n = 132 and 80 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for A177U mutant strain; n = 81 and 82 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for G178A mutant strain; n = 88 and 83 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for G178U mutant strain; n = 91 and 97 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for U181A mutant strain; n = 101 and 94 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for U182A mutant strain; n = 84 and 88 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for G184A mutant strain; n = 117 and 104 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for G184A–C195U mutant strain; n = 82 and 88 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for G215A mutant strain; n = 90 and 84 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for U224A mutant strain; n = 92 and 100 cells examined over two independent experiments after 0 and 20 min induction for U224G mutant strain. g Comparison of the SgrS regulation efficacy calculated from Sort-Seq assay and the imaging-based analysis. Error bars in the x-axis are standard deviations calculated from two experimental replicates and those in the y-axis are as described in f. The fitting is shown in blue and the gray region shows the 95% confidence region. Pearson’s R = 0.71; 95% CI = 0.39, 0.88; P = 0.021, two-sided t test. Source data are provided as a Source data file.