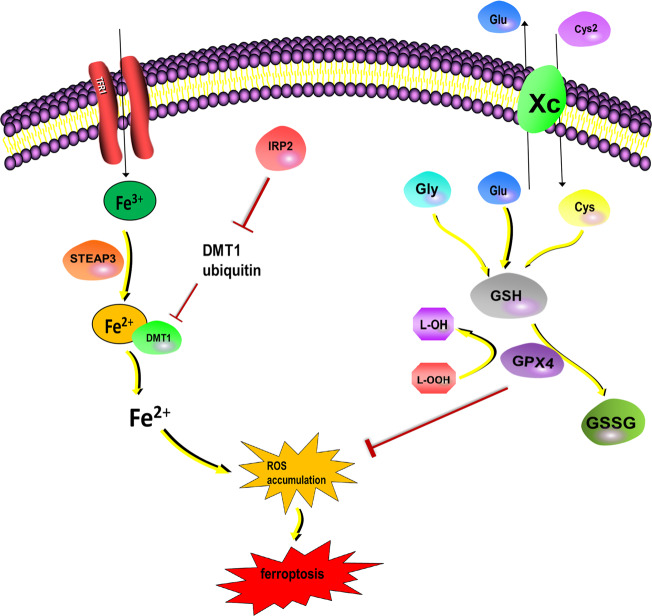
Fig. 4. Cellular ferroptosis.
The related lipid peroxidation pathway mediated by GPX4 plays an important role in inhibiting ferroptosis. System Xc—is a cystine/glutamate antiporter that transports intracellular Glu to the outside of the cell and transfers extracellular Cys2 into the cell. Then, Cys2 is converted into Cys for the synthesis of GSH. GPX4 converts GSH into oxidized GSSG and reduces cytotoxic lipid peroxide (L-OOH) to the corresponding alcohol (L-OH), which ultimately reduces ROS accumulation. On the other hand, Fe3+ enters the cell and is reduced to Fe2+ by the iron oxidoreductase STEAP3. Then, DMT1 causes Fe2+ release from the endosome, leading to ROS accumulation, which in turn leads to lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. IRP2 (IREB2) can inhibit the ubiquitination of TfR1 and divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) to increase cellular iron uptake and promote ferroptosis.