Figure 1. WIN site inhibitor selectively displaces proteins from WDR5.
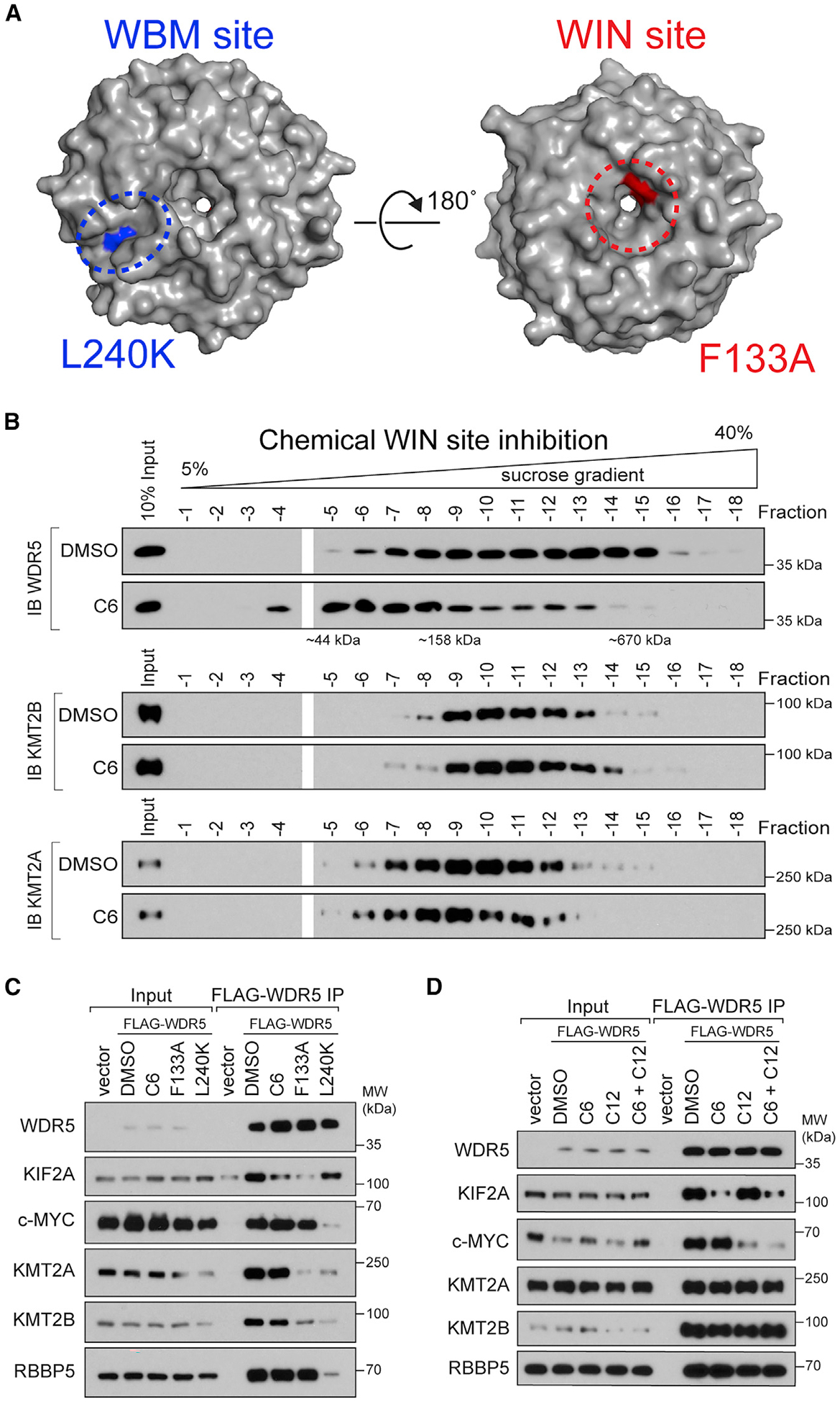
(A) Crystal structure of WDR5 (PDB: 2H14) outlining the location of the WBM site (blue) and the WIN site (red); locations of the L240K and F133A mutations are also shown.
(B) Density sedimentation analysis of HEK293 cells treated for 5 h with 30 μM C6 or DMSO. After treatment, cells were lysed and extracts analyzed by sucrose gradient density sedimentation followed by immunoblotting (IB) for WDR5 (top), KMT2B (middle), or KMT2A (bottom). Positions of molecular weight markers are indicated. n = 3 biological replicates.
(C) HEK293 cells stably expressing wild-type (WT) FLAG-tagged WDR5, or the indicated mutant, were treated with DMSO or 30 μM C6 for 5 h, WDR5 was recovered by FLAG IP, and the co-precipitating proteins detected by IB. Inputs are 5% for RBBP5 and WDR5, 3% for KMT2A and KMT2B, and 1% for KIF2A and c-MYC; n = 3 biological replicates.
(D) Lysates from cells stably expressing WT FLAG-tagged WDR5 were treated with DMSO (0.1%), 5 μM C6, 50 μM C12, or both 5 μM C6 and 50 μM C12, for 5 h; WDR5 was recovered by anti-FLAG IP and IB performed for the indicated proteins. Inputs are 5% for RBBP5 and WDR5, 3% for KMT2A and KMT2B, and 0.5% for KIF2A and c-MYC; n = 4 biological replicates.
See also Figure S1.
