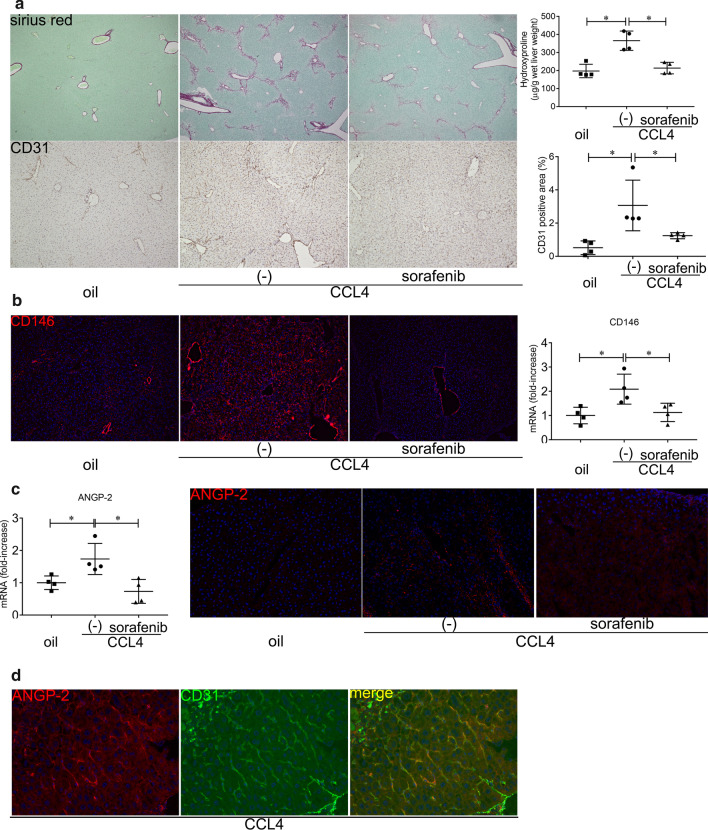
Fig. 2.
ANGP-2 expression in mouse liver fibrosis induced by CCl4. BALB/c male mice were treated with CCl4 (1 mL/kg twice a week) with or without sorafenib (750 μg 3 times a week) for 2 weeks and humanely sacrificed. a Collagen deposition was assessed by Sirius Red staining (original magnification: × 40) and hydroxyproline content in the liver (upper panels). CD31 expression in the liver was examined by immunohistochemistry (original magnification: × 100), and the CD31-positive area (%) was quantified (lower panels). b CD146 expression in the liver was examined by immunohistochemistry using the anti-PE-conjugated CD146 antibody (original magnification: × 100) (left panels). CD146 expression in the liver was determined by real-time qRT-PCR (right panel). c ANGP-2 mRNA expression in the liver was determined by real-time qRT-PCR (left panel). ANGP-2 was stained with a primary antibody and an Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated secondary antibody (original magnification: × 200) in the liver (right panels). d ANGP-2 and CD31 in the liver were double stained with the following antibodies: anti-ANGP-2 antibody, Alexa Fluor 546-conjugated secondary antibody, and FITC-conjugated anti-CD31 antibody (original magnification: × 400). The two images were merged to demonstrate ANGP-2 expression in LSECs. The results are representative of at least four independent experiments and provided as means ± SDs. *P < 0.05 based on a one-way ANOVA. The values for Spearman’s or Pearson’s correlation coefficient are indicated