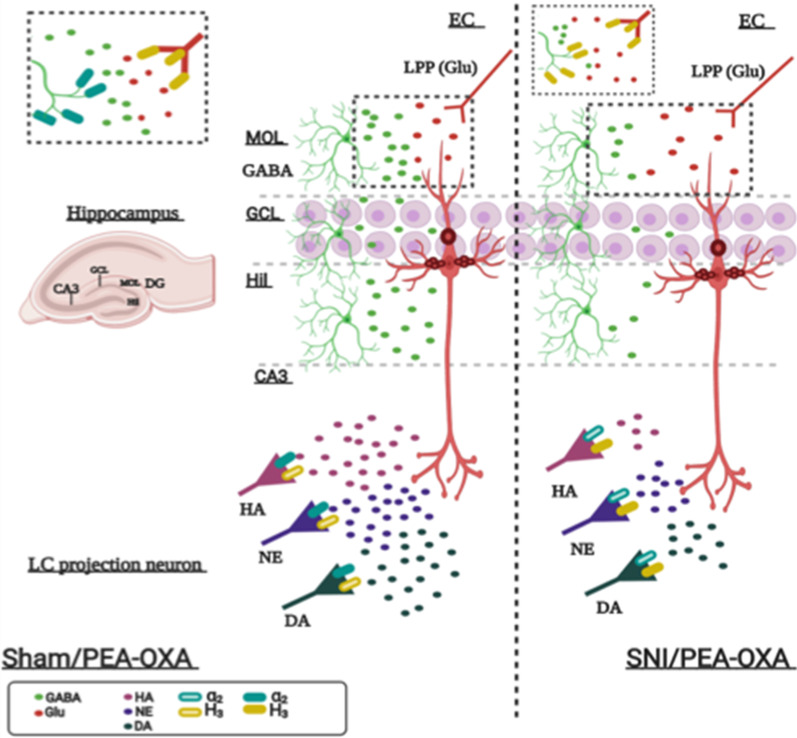
Fig. 8.
The illustration shows the effect of PEA-OXA on the release of amino acids and biogenic amines in the hippocampus DG and CA3 in sham and SNI mice. In sham mice (left), chronic treatment with PEA-OXA reduces glutamate and increases GABA release in the DG. These effects are due to the action of PEA-OXA as a partial agonist on histamine H3 heteroreceptors, yellow filled rectangles and as an antagonist on alpha2 adrenergic heteroreceptors, blue filled rectangles, respectively on the glutamatergic and GABAergic terminals. An enlargement corresponding to the dotted box is shown at the top left. In the CA3 of sham mice PEA-OXA causes an increase in the levels of histamine, dopamine and norepinephrine, an action due to the blocking of the adrenergic alpha2 heteroreceptor. In SNI mice (right), PEA-OXA reduces the levels of glutamate (Glu) and GABA in the molecular layer (MOL), granular cell layer (GCL) and hilus (Hil) of the DG, an effect due to the stimulation of the histamine H3 heteroreceptor. An enlargement corresponding to the dotted box is shown at the top left. In the CA3 of SNI mice the chronic treatment with PEA-OXA decreases (and normalizes) the levels of histamine while increases (and normalizes) those of dopamine and norepinephrine, an action due to the stimulation of histamine H3 autoreceptor and heteroreceptor on histaminergic and cathecolaminergic terminals, respectively, arriving from LC. The PEA-OXA, being a partial agonist in presence of high levels of histamine observed in the SNI, acts as an antagonist. The glutamatergic pyramidal neuron, the glutamatergic projection fiber from the entorhinal cortex (lateral perforating path, LPP) and the extracellular glutamate are painted in red, the GABAergic interneurons and the extracellular GABA in green, the histaminergic (HA), noradrenergic (NE) and dopaminergic (DA) projection neurons are painted in pink, purple and dark green, respectively. A representation of the organization of the different hippocampal subregions is shown in the left panel