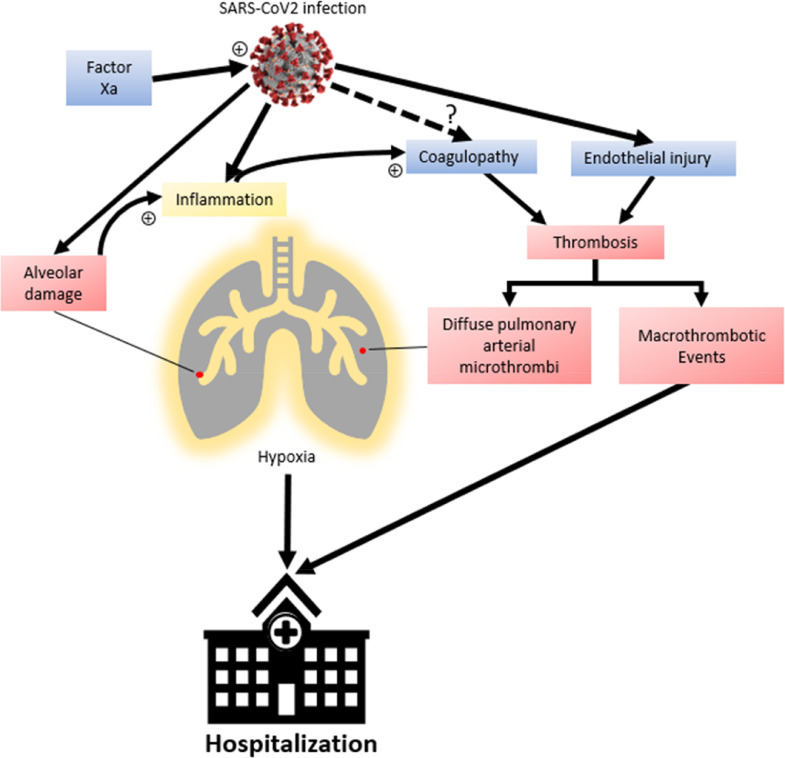
Figure 1.
Coagulopathy and COVID-19 pathogenesis. Coagulopathy and diffuse pulmonary microthrombi have been documented in COVID-19. While coagulopathy is a known consequence of inflammatory changes, it is unclear if SARS-Co-V-2 independently affects hypercoagulability. Coagulopathy, along with viral endothelial injury, leads to diffuse pulmonary microthrombi which may potentiate pulmonary injury in addition to alveolar damage from SARS-Co-V-2 infection as well as macrothrombotic events. Factor Xa can also play a role in cell entry and infection by SARS-Co-V-2, and therefore viral propagation. Outpatient anticoagulation with rivaroxaban, a specific Factor Xa inhibitor, has the potential to prevent thromboembolic events as well as pulmonary microthrombi and progression of pulmonary insufficiency in COVID-19, reducing the need for hospitalization.