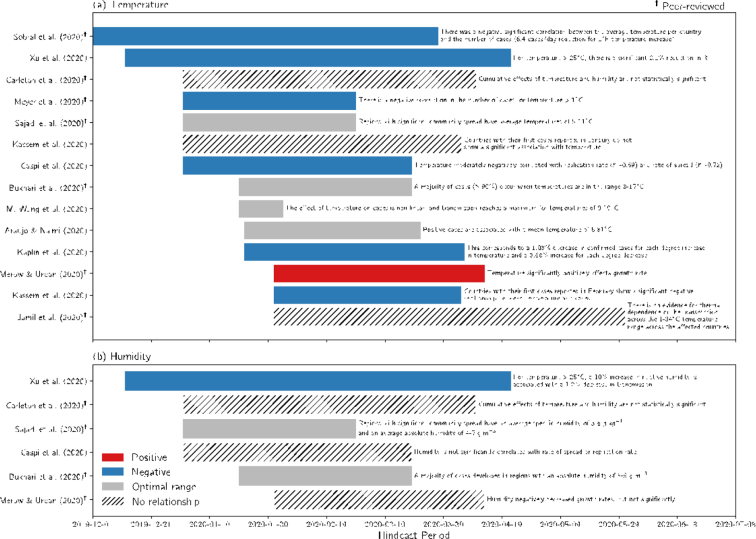
Fig. 2.
Studies focusing on the sensitivity of COVID-19 to (a) temperature and (b) humidity over the global domain versus their hindcast period. Studies are shaded by the sign or result of their key finding, and a brief summary of the study is provided. A positive relationship implies that increasing temperature or humidity is associated with additional COVID-19 cases or other COVID-19 transmission metrics, while the opposite is true for a negative relationship. Several studies do not provide directionality but rather report an optimal range.