Fig. 2 |. PI3K signaling genes PIK3CA, PTEN and MTOR are frequently mutated in sporadic CH.
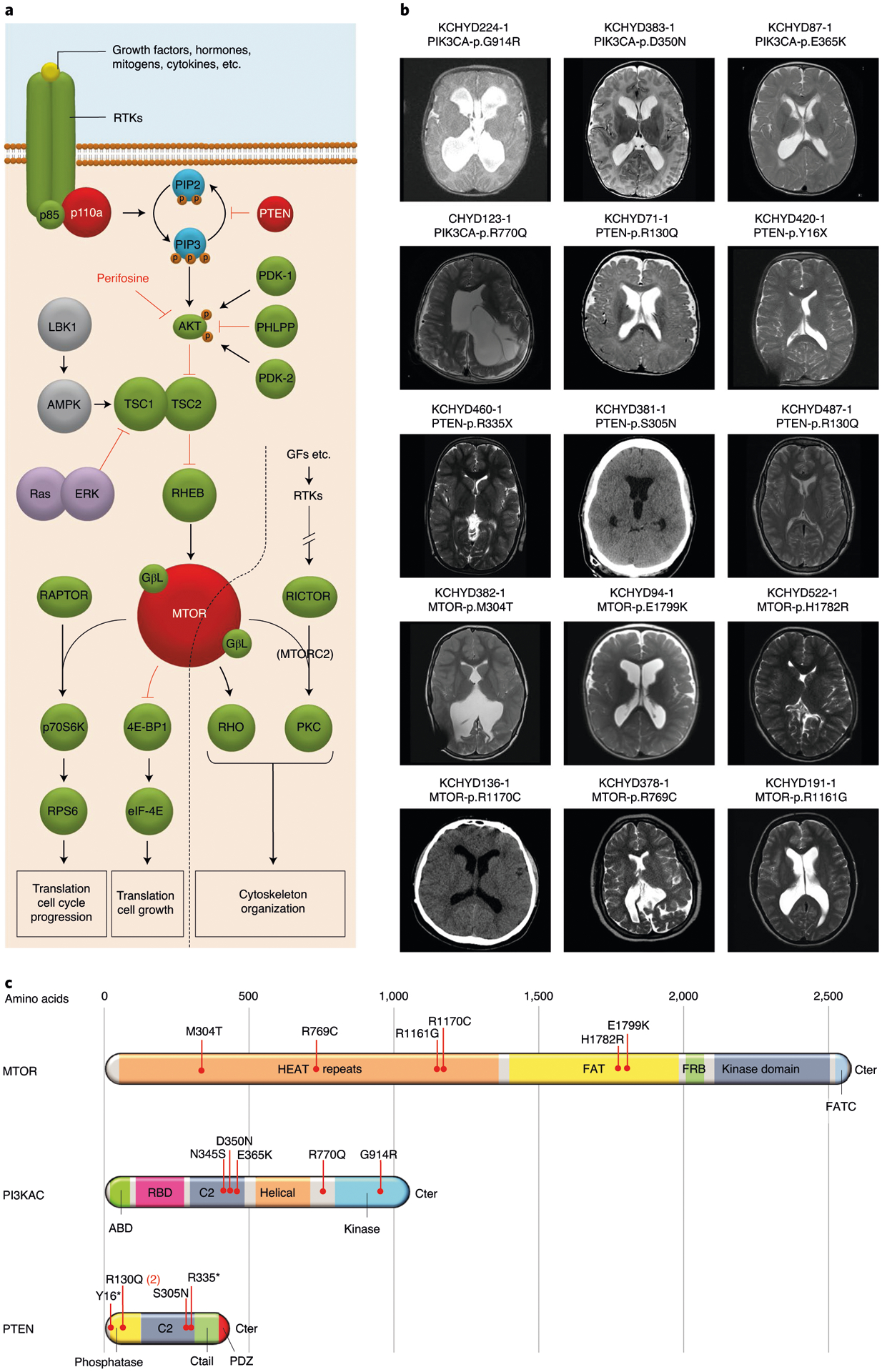
a, Depiction of the PI3K signaling pathway with genes mutated in sporadic CH indicated by a red-filled circle. PIK3CA and PTEN mutations are anticipated to lead to increased PIP3 production and mTOr activation, effects mimicked by CH-associated MTOR mutations. PI3K signaling regulates growth, proliferation and differentiation of embryonic and early postnatal NSCs. GF, growth factor; rTK, receptor tyrosine kinase. b, representative T1 or T2-weighted axial brain mrIs or head CT images of neurosurgically treated CH probands with the indicated PIK3CA, PTEN and MTOR mutations (Supplementary Table 11 and extended Data Figs. 3–5 contain clinical and neuroradiographic details for each patient). c, mutation mapping of PIK3CA, PTEN and MTOR mutations in relation to critical functional domains in each molecule. Frb, FKbP12-rapamycin-binding domain; FATC, C-terminal FAT domain. AbD, adaptor-binding domain; rbD, ras-binding domain; PDZ, PSD95, DLG1 and ZO1 domain.
