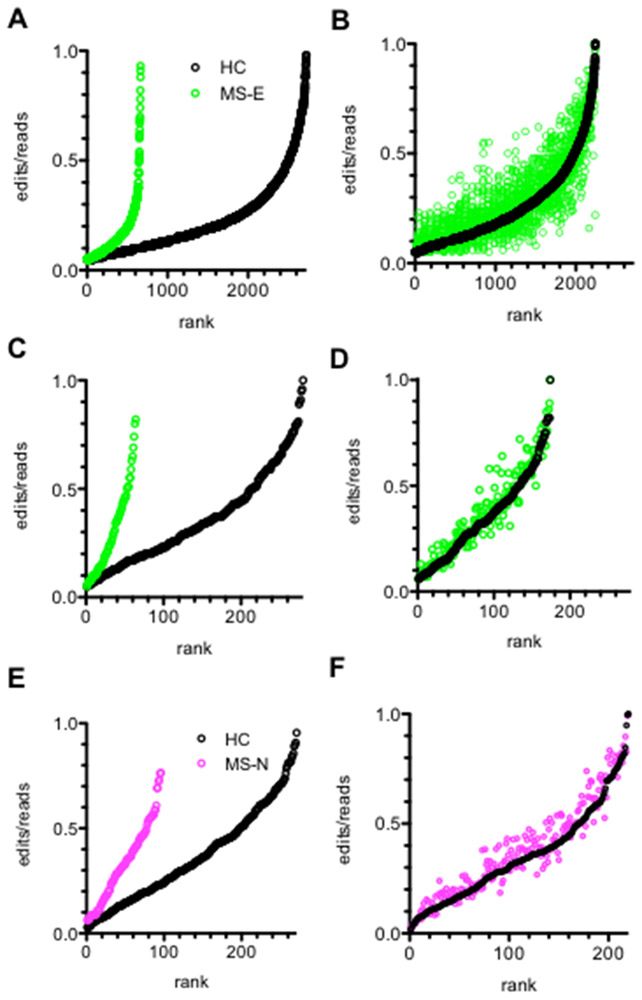
FIGURE 2.
Loss of genome-wide A-to-I editing in MS. (A) Unique A-to-I editing sites present in ≥ 2 HC samples and 0 MS-E samples ranked according to edit/read ratio (Y-axis, black open circles) or present in ≥ 2 MS-E samples and 0 HC samples (open green circles). (B) Number of unique sites that are A-to-I edited in both ≥ 2 HC and ≥ 2 MS-E samples ranked according to HC edit/read ratios (open black circles; corresponding MS-E edit/read ratios at the identical nucleotide sites are also shown (open green circles) (C) Number of unique A-to-I editing sites present in all 8 HC samples and 0 MS-E samples ranked according to edit/read ratios (Y-axis, black open circles) or present in all 8 MS-E samples and 0 HC samples (open green circles). (D) Number of unique sites that are A-to-I edited in all 8 HC and all 8 MS-E samples ranked according to HC edit/read ratios (open black circles; corresponding MS-E edit/read ratios at the identical nucleotide sites are also shown (open green circles). (E) Unique A-to-I editing sites present in all 8 HC samples and 0 MS-N samples ranked according to edits/read ratios (Y-axis, black open circles) or present in all 8 MS-N samples and 0 HC samples (open magenta circles). (F) Number of unique sites that are A-to-I edited in all 8 HC and all 8 MS-N samples ranked according to HC edit/read ratios (open black circles); corresponding MS-E edit/read ratios at the identical nucleotide sites are also shown (open magenta circles).