Figure 5.
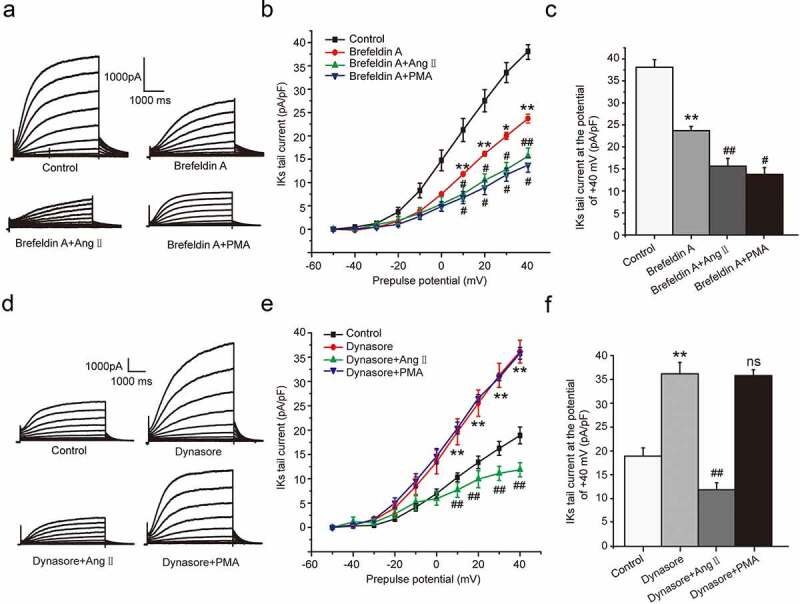
The molecular mechanism underlying the chronic inhibition of Ang II and PMA on IKs current in HEK 293B cell. (a) The representative IKs current by the Ang II and PMA treatment under the channel forward transport inhibition. (b) The current–voltage relationship for the IKs current by the Ang II and PMA treatment under the channel forward transport inhibition. (c) The summary data for the tail currents by the Ang II and PMA treatment under the channel forward transport inhibition at +40 mV prepulse. (d) The representative IKs current by the Ang II and PMA treatment under the channel endocytosis inhibition. (e) The current–voltage relationship for the IKs current by the Ang II and PMA treatment under the channel endocytosis inhibition. (f) The summary data for the IKs tail currents by the Ang II and PMA treatment under the channel endocytosis inhibition at +40 mV prepulse. (**P < 0.01, compared with the control group; ##P < 0.01, compared with Brefeldin A or Dynasore group; #P < 0.05, compared with Brefeldin A group)
