Figure 2.
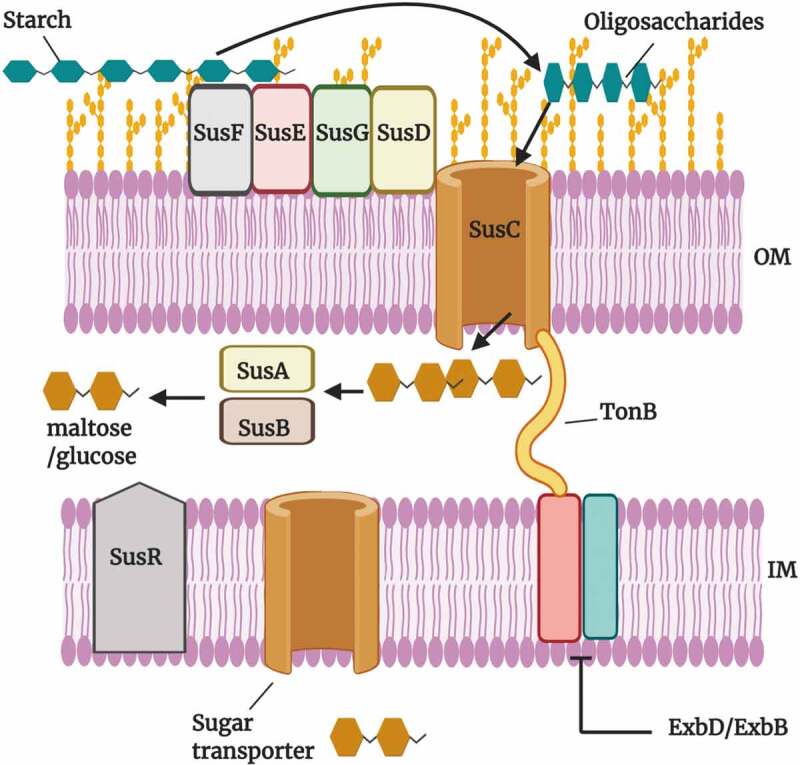
The starch utilization system (Sus) of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron.
SusC is a TonB-dependent transporter that works in collaboration with the starch bindinglipoproteins SusD, SusE and SusF. These lipoproteins play roles in binding and immobilizing the extracellular starch polymers. Subsequently, SusG, an α-amylase, degrades the starch into smaller oligosaccharides which proceed to the periplasm via SusC. In the periplasm, SusA (α-amylase) and SusB (α-glucosidase) breakdown the oligosaccharides into maltose and glucose. These di- and mono-saccharides are transported into the cytoplasm via sugar transporting permeases. The sensor/regulator, SusR, (sensor domain in the periplasm; DNA binding domain in the cytoplasm) regulates the expression of the susA-G genes in response to maltose in the periplasm. The Sus system of Bth gives it an advantage in the competitive gut environment and also assists in the attachment to mucus glycans.
